Operational Amplifier
An operational amplifier is basically a three-terminal device that consists of two high-impedance inputs. One of the inputs is called the Inverting Input, marked with a negative, the other input is called the Non-inverting Input, marked with a positive.
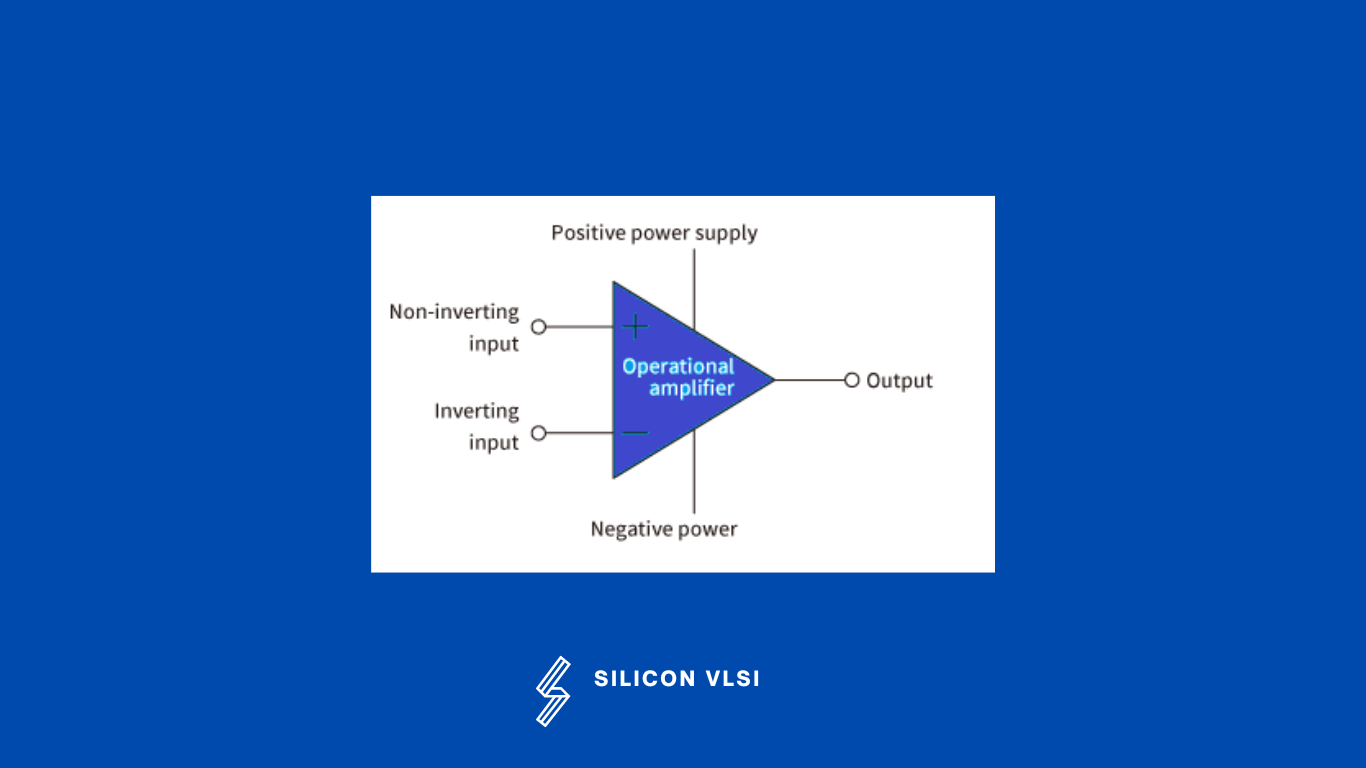
Important characteristics of an operational amplifier
- Very high gain #
- Very high input impedance #
- Very low output impedance
- Common Mode Rejection Ratio
What is the function of the operational amplifier?
An integrated circuit called an operational amplifier has the ability to amplify weak electric impulses. One output pin and two input pins make up an operational amplifier. The voltage difference between the two input pins is amplified and output by it as its primary function.
What is operational amplifier and its types?
- Dual supply
- Single supply
- Rail-to-rail.
What are the advantages of op-amp?
- Increased circuit stability
- Increased input impedance
- Decreased output impedance
- Increased frequency bandwidth at a constant gain.
Is op-amp negative or positive?
Op-amps are frequently employed in negative feedback applications. Negative comments are briefly discussed in this section. There are two types of feedback loops: positive and negative.
What is Infinite Loop
Infinite loop gain is a limit of the open loop gain GG of an ideal operational amplifier. As the open loop gain tends to infinity, the voltage difference between the inputs tends to zero.
What is Input Offset Voltage?
The Input Offset Voltage is defined as the voltage that must be applied between the two input terminals of the op-amp to obtain zero volts at the output.
Why offset voltage is used?
The difference in voltage between the outputs of two operation amplifiers, or op amps, produces offset voltage. It exists in every real-world circuit where there are two op amps with opposing charges of the same value that are grounded but nonetheless produce a tiny charge that is not quite zero.