Difference Between CPLD and FPGA: Architecture, Features, and Applications
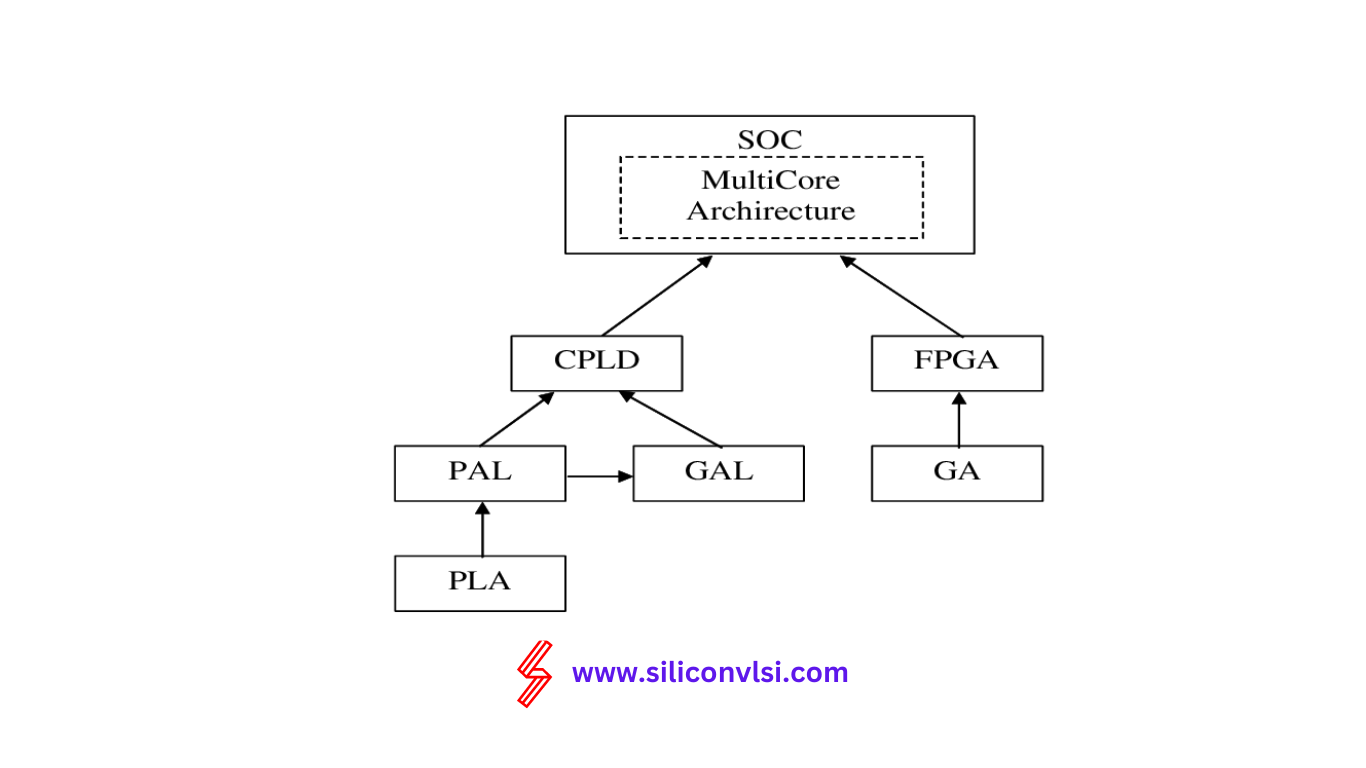
CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device) and FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) are both programmable logic devices used in digital circuit design, but they differ in architecture, capabilities, and applications. A CPLD is suitable for simpler, lower-density logic designs and is known for faster start-up time and predictable performance. In contrast, an FPGA offers higher logic capacity, more flexibility, and is ideal for complex, high-performance applications. Understanding the difference between CPLD and FPGA is essential for choosing the right solution based on project requirements.
A Field-Programmable Gate Array, or FPGA, is a flexible type of Field-Programmable Device (FPD) designed with a generic structure that allows for a significant increase in logic capacity. When you compare FPGAs to Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDs), you’ll notice that FPGAs offer narrower logic resources. While CPLDs feature resources with several inputs (like AND planes), FPGAs provide a much larger ratio of flip-flops to logic resources. This means that when you choose an FPGA, you’re likely to gain more flexibility and performance for your specific design needs.
| Feature | CPLD | FPGA |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Programmable logic blocks (PLBs) | Configurable logic blocks (CLBs) |
| Programmable interconnects | Programmable interconnects | |
| Macrocells | I/O blocks | |
| Functionality | Suitable for small to medium-scale | Suitable for complex and large-scale designs |
| designs | ||
| A limited number of macrocells | The high number of CLBs | |
| Relatively simple logic functions | Supports complex logic functions and | |
| arithmetic operations | ||
| Flexibility | Fixed structure and limited | Highly flexible and customizable |
| customization options | ||
| Well-suited for designs with static | Supports dynamic reconfiguration and | |
| logic | iterative design processes | |
| Time-to-Market | Shorter design and verification cycles | Longer design and verification cycles |
| Faster production turnaround | Slower production turnaround but offers | |
| greater flexibility in design changes | ||
| Power Consumption | Generally lower power consumption | Higher power consumption |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost compared to CPLD |
| Application | Control systems | Digital signal processing (DSP) |
| Examples | Simple logic functions | High-performance computing |
FAQs
Can I use a CPLD instead of an FPGA for a large-scale design? It is generally not recommended to use a CPLD instead of an FPGA for a large-scale design. CPLDs have limited macrocells and are better suited for smaller designs. FPGAs offer a higher number of configurable logic blocks (CLBs) and provide more flexibility for complex designs.
Are CPLDs and FPGAs compatible with each other? CPLDs and FPGAs are not directly compatible with each other due to differences in their architectures and programming methodologies. However, they can be used together in a system design where the CPLD handles specific functions while the FPGA handles more complex tasks.
Which device is more suitable for low-power applications? CPLDs are generally more suitable for low-power applications. They have lower power consumption compared to FPGAs, making them a better choice when power efficiency is a critical factor.
Can I reconfigure an FPGA during runtime? Yes, FPGAs support dynamic reconfiguration, which allows for modifications to the circuit configuration during runtime. This feature provides flexibility for design changes and reconfigurable computing.
Are CPLDs and FPGAs used in the same industries? CPLDs and FPGAs find applications in various industries, including telecommunications, aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial automation. While they have overlapping applications, the choice between CPLDs and FPGAs depends on the specific requirements and design constraints of each industry.