Twisted Pair Cable
Twisted Pair Cable is a type of wiring used for data transmission, consisting of two conductors twisted together to form a circuit. It typically comprises two insulated copper wires that carry data as electric signals. Twisted Pair Cable is commonly used in Local Area Networks (LANs) and comes with both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Twisted Pair Cable
- Low Cost: Twisted Pair Cable is cost-effective compared to other cable types.
- Flexibility: It is highly flexible and easy to install, making it a preferred choice for networking.
- Familiarity: Twisted Pair Cable is a well-established technology widely used in networking.
- Ease of Termination: It is simple to terminate, facilitating easy installation and maintenance.
Disadvantages of Twisted Pair Cable
- Limited Bandwidth: Twisted Pair Cable has limited bandwidth, which restricts its transmission speed and data capacity.
- Interference: It is susceptible to electromagnetic interference, leading to signal degradation and loss.
- Limited Distance: Twisted Pair Cable has a restricted transmission distance, making it unsuitable for large networks.
- Security: Twisted Pair Cable is vulnerable to eavesdropping and interception, compromising network security.
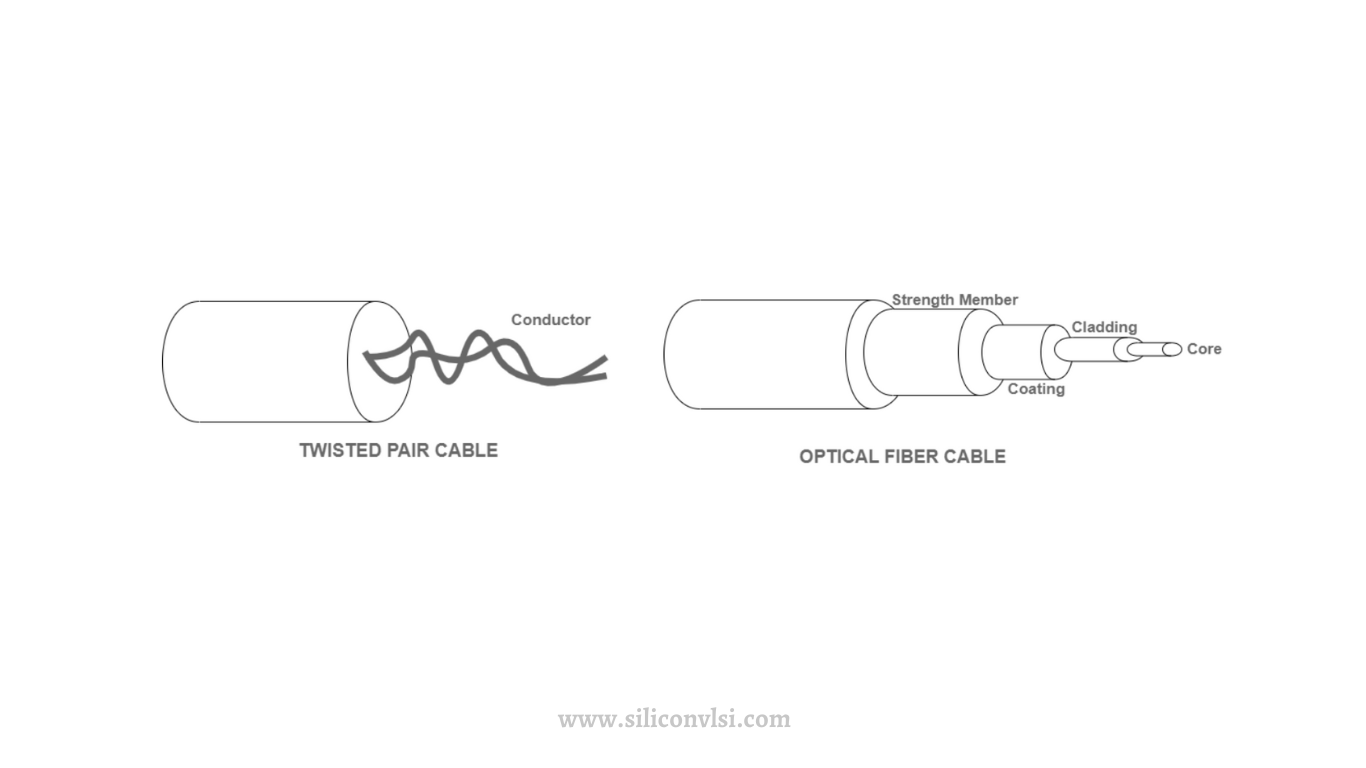
Optical Fiber Cable
Optical Fiber Cable is a guided media used for long-distance transmission and high-performance data networking. It consists of very thin glass fibers bundled together in a single cable. In optical fiber cable, data is transmitted as pulses of light. Optical Fiber Cable is commonly used in long-distance networks and large data centers.
Advantages of Optical Fiber Cable
- High Bandwidth: Optical Fiber Cable offers a high bandwidth, making it suitable for high-speed data transfer.
- Long Distance: It can transmit data over long distances without signal loss.
- Security: Optical Fiber Cable is difficult to tap into, ensuring secure data transmission.
- Immunity to Interference: It is immune to electromagnetic interference, maintaining signal integrity.
Disadvantages of Optical Fiber Cable
- Cost: Optical Fiber Cable is more expensive than other cable types.
- Installation: Installing optical fiber cables requires specialized equipment and expertise, making it challenging.
- Fragility: Optical Fiber Cable is fragile and prone to breakage, potentially leading to data loss.
Similarities between Twisted Pair Cable and Optical Fiber Cable
- Both can be used for data transmission over long distances.
- Both aim to minimize signal interference and distortion.
- Both have various categories or types offering different performance levels and data transfer rates.
- Both require connectors for termination and device connections.
- Both are commonly used in LANs and WANs for data, voice, and video transmission.
- Both are available in various lengths to accommodate installation requirements.
- Both have specific installation requirements, including handling, termination, and testing.
- Both can be affected by environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and electromagnetic interference.
Differences between Twisted Pair Cable and Optical Fiber Cable
- Conductor Material:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Uses copper wires for signal transmission.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Uses glass fibers to transmit signals as pulses of light.
- Cable Diameter:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Has a larger diameter compared to optical fiber cable.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Has a small and thin diameter.
- Attenuation (Signal Loss):
- Twisted Pair Cable: Experiences significant attenuation.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Experiences minimal attenuation.
- Installation Difficulty:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Easy and simple to install.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Challenging to install, requiring expertise.
- Use Cases:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Suited for wire shielding and data networks, often used in LANs.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Primarily used in long-distance networks between cities and countries.
- Cost:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Comparatively inexpensive.
- Optical Fiber Cable: More expensive due to its performance and capacity.
- Bandwidth:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Supports lower bandwidth.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Supports very high bandwidth.
- Noise Immunity:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Has low noise immunity.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Has high noise immunity compared to twisted pair cable.
- Security:
- Twisted Pair Cable: This does not guarantee signal security.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Provides secure data transmission.
- Loss Types:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Can experience resistive loss, radiated loss, and dielectric loss.
- Optical Fiber Cable: Can experience dispersion, bending, absorption, and attenuation losses.