Mixed-Signal Layout Strategies: Balancing Digital and Analog Circuitry
In the realm of integrated circuit (IC) design, where both digital and analog functionalities coexist, meticulous attention to layout considerations is vital, especially to maintain the integrity of sensitive analog nodes in a potentially noisy digital environment. This fusion of digital and analog circuits presents challenges that need to be addressed to ensure optimal performance. Below, we delve into various strategies for successful mixed-signal layout:
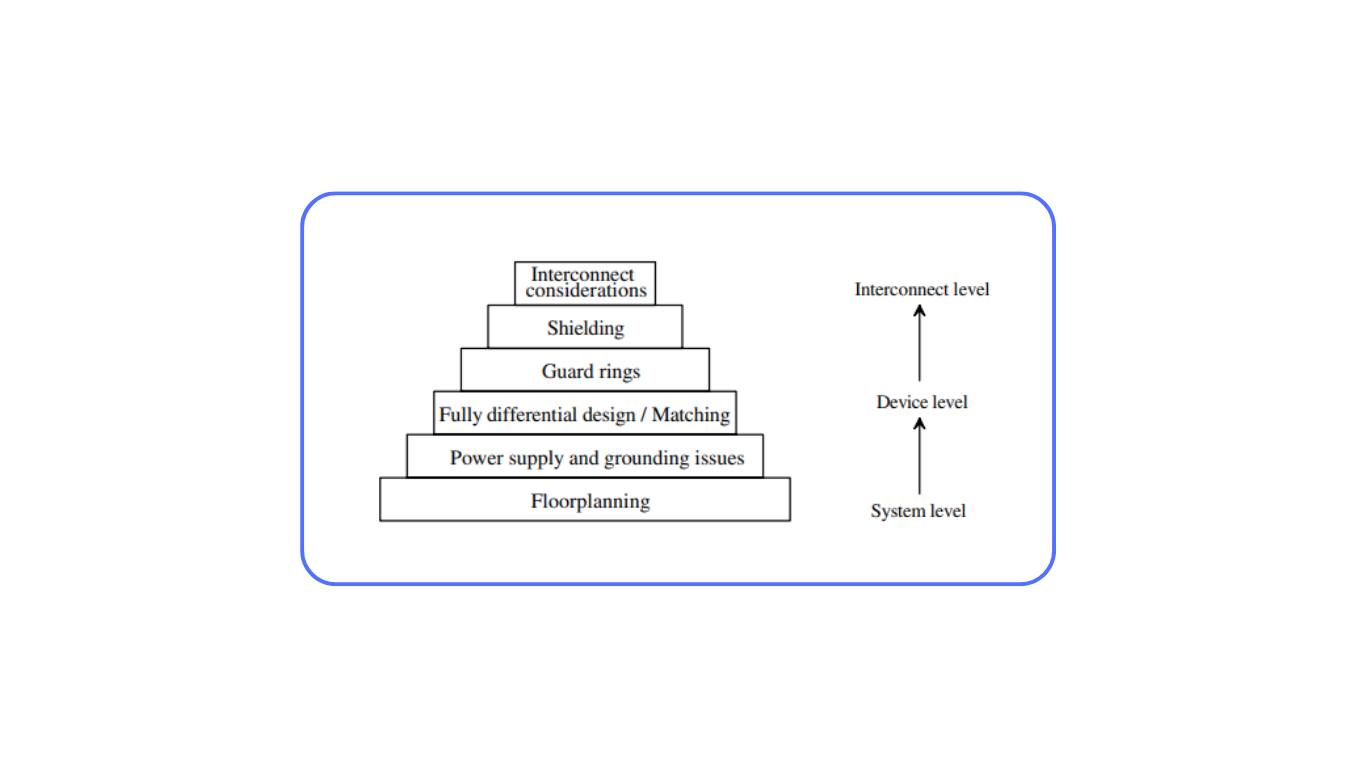
Floorplanning
The first step in mixed-signal layout involves floorplanning, where the arrangement of components is strategically considered. It’s crucial to categorize analog components by their sensitivity to noise. For instance, high-impedance nodes, typically associated with input signals, are highly sensitive and require shielding from digital signals. Conversely, high-swing analog circuits like comparators should be positioned between sensitive analog and digital circuitry.
Power Supply and Grounding
Sharing power supply and ground connections between digital and analog circuits can lead to noise injection. To minimize interference, separate routing channels for power and ground should be provided for both types of circuits. In an ideal scenario, separate pins and pads for analog and digital components can be used, ensuring complete decoupling. Careful consideration must also be given to reduce resistance and inductance in the connections to mitigate voltage spikes.
Fully Differential Design
For operational amplifiers and similar circuits, a fully differential approach is beneficial. By injecting equal noise into both differential amplifiers, the common-mode rejection inherent in these circuits helps eliminate or minimize the noise. Achieving this balance relies on matching the transistors in the amplifier, emphasizing the importance of layout techniques like common-centroid and interdigitated designs.
Guard Rings
Implementing guard rings is essential for isolating sensitive circuits from noise sources. Analog circuits, especially those processing low-level signals, should be placed in a separate well if possible, with guard rings connected to the analog VDD supply. For digital circuits, guard rings around n-channel devices can also help minimize noise transmission.
Shielding
Shields can be introduced between signal layers to prevent the coupling of sensitive analog signals with noisy digital ones. If crossing is unavoidable, consider carrying digital signals on the top metal layer, while analog signals use lower layers. A metal strip connected to analog ground can act as a shield between them.
Other Interconnect Considerations
Additional layout strategies include minimizing the lengths of current-carrying paths for analog circuitry to reduce voltage drop due to resistance. Liberal use of vias and contacts for layer transitions helps reduce resistance and enhance reliability. Avoid routing current-carrying signal paths using the poly layer, as it has higher resistance and introduces additional contact resistance.
In summary, a successful mixed-signal layout involves meticulous planning, segregation of analog and digital components, robust power supply and grounding solutions, shielding to prevent interference and careful routing strategies. These considerations, combined with a focus on noise reduction, ensure that both digital and analog circuits can coexist harmoniously on the same IC substrate, resulting in optimal performance and minimal signal degradation.
How can floorplanning impact the performance of a mixed-signal circuit?
Floorplanning can significantly affect circuit performance. During mixed-signal system design, factors such as the sensitivity of analog signals to noise, the placement of sensitive analog components, and the separation of high-swing analog circuits from digital components should be considered in the floorplan analysis.
What challenges arise when analog and digital circuits share the same power supply and ground connections?
Sharing power supply and ground connections between analog and digital circuits can introduce noise from the digital system into the sensitive analog circuitry. To mitigate this, careful consideration should be given to power and ground routing. Options include separating the interconnects for analog and digital circuits or using separate pads and pins for each.
How does the use of guard rings enhance the performance of mixed-signal circuits?
Guard rings can help minimize noise in mixed-signal circuits. Sensitive circuits should be placed in separate wells if possible, with guard rings attached to the respective power supplies (analog or digital). Guard rings around n-channel digital devices can also reduce noise transmission.
What role does shielding play in reducing noise in mixed-signal circuits?
Shielding can protect sensitive analog signals from digital switching noise. Avoiding the crossing of sensitive analog signals with digital signals is ideal. If unavoidable, using the top metal layer for digital signals and adding a metal layer with a connection to the analog ground between the two can help minimize noise.
What additional layout strategies can improve analog circuit performance?
Minimizing the length of current-carrying paths, using vias and contacts liberally, and avoiding poly for current-carrying paths can incrementally improve analog circuit performance. However, these strategies are less effective if earlier strategies related to floorplanning, power supply, and grounding are not followed, as noise and interference can still impact performance.