Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
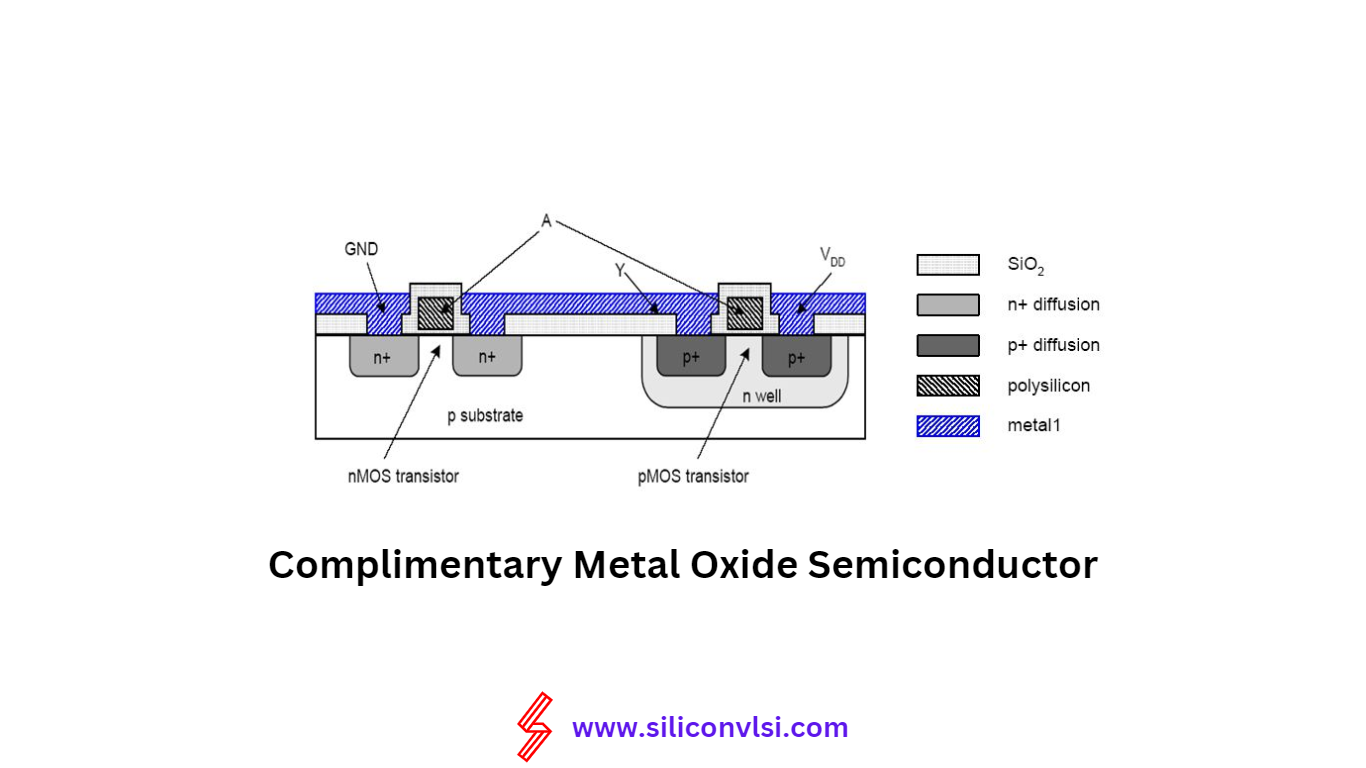
CMOS Applications and Advantages: CMOS stands for Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor, and it refers to a logical circuit constructed with Metal Oxide Semiconductor technology. CMOS is the most commonly used technology for building digital integrated circuits. The applications of CMOS Logic have been previously listed.
A CMOS circuit is built using both N-type and P-type semiconductors in a complementary manner. There are three well-known types of MOS technology: PMOS, NMOS, and CMOS. CMOS logic offers several advantages over the others.
CMOS Advantages
The main advantages of CMOS logic circuits are as follows:
- Very low static power consumption
- Low power dissipation
- Minimal heat production
- Ultra-fast switching operations
- Very high noise margins
- Wide range of operating voltage
In a CMOS logic circuit, the transistors operate in a complementary fashion. When one transistor turns on, the other turns off. The basic CMOS circuit includes two transistors: the P-Channel MOSFET and the N-Channel MOSFET. The source terminal of the P-Channel MOSFET connects to the positive voltage (Vdd), while the source terminal of the N-Channel MOSFET connects to the ground. The drain terminals of both transistors are connected together and used as the input terminal. CMOS circuits are typically built with enhancement type MOSFETs.
The transistors used in CMOS have a threshold voltage below which the current flow gradually decreases. Static CMOS circuits are highly power-efficient, dissipating almost zero power except during switching. They also generate very little heat.
Since digital circuits operate with low power, leakage current becomes a significant concern. In the case of CMOS logic, leakage current is almost negligible, thereby not impacting total power consumption.
CMOS logic exhibits duality in its characteristics due to its construction with PMOS and NMOS transistors. NAND gates and OR gates are commonly built using CMOS logic. In a NAND gate, when both inputs are high, the NMOS transistors conduct current while the PMOS transistors do not. Likewise, when both inputs are low, the NMOS transistors do not conduct current, but the PMOS transistors do. When one of the inputs is low, one of the NMOS transistors turns off.
CMOS Applications
The most common uses of CMOS technology include:
- Computer CPUs
- Image sensors
- Digital microchips
- Electronic register circuits
- Microcontrollers
- Flash memory
- CMOS batteries
- Data converter circuits
- RF CMOS for RF circuits
