Crosstalk and Shielding
Crosstalk between the nets may severely degrade the performance of an analog circuit. thus, it is required to extract these effects during the routing. Due to crosstalk phenomena, sometimes we need to do shielding.
Shielding reduces crosstalk. In RF circuits, inductive coupling may also be critical for the performance and RLC models for interconnects, such as in are used to observe these inductive effects. Even EM simulations may be carried out to observe the parasitic effects more accurately
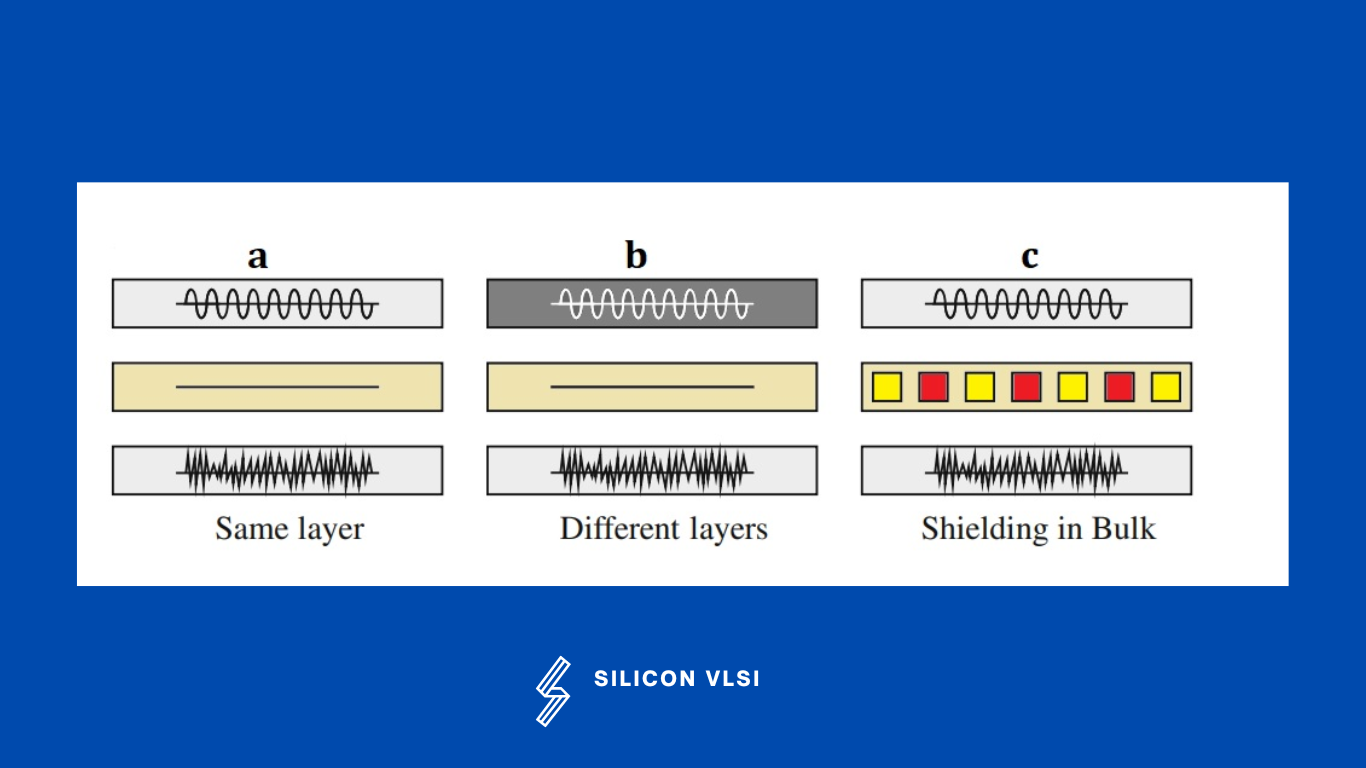
The long wires running in parallel affect the performance of the analog circuits. One way to reduce the crosstalk between these wires is to add space between them. If it is impossible to reduce the coupling by adding space, the router may introduce a shield between the critically coupled nets. To avoid the crosstalk, add a shield line between wires as shown in the above figure. In the above Figure, Three, different shielding methods are displayed. These methods may be used to reduce the crosstalk via the bulk or routing layers.
Crosstalk Prevention techniques
- Do shielding. #
- Increase the spacing between the aggressor and victim net.
- Downsize the aggressor cell or Upsizing the victim cell
![]()
What is the use of shielding in VLSI?
Interconnect shielding is employed in Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) designs to prevent noise interference among signals. This technique involves using shielding wires connected to the power supply voltage, which run adjacent to signal wires. By doing so, it mitigates signal switching-induced noise through cross-coupling capacitance to neighboring signals.