Clock Skew and Uncertainty
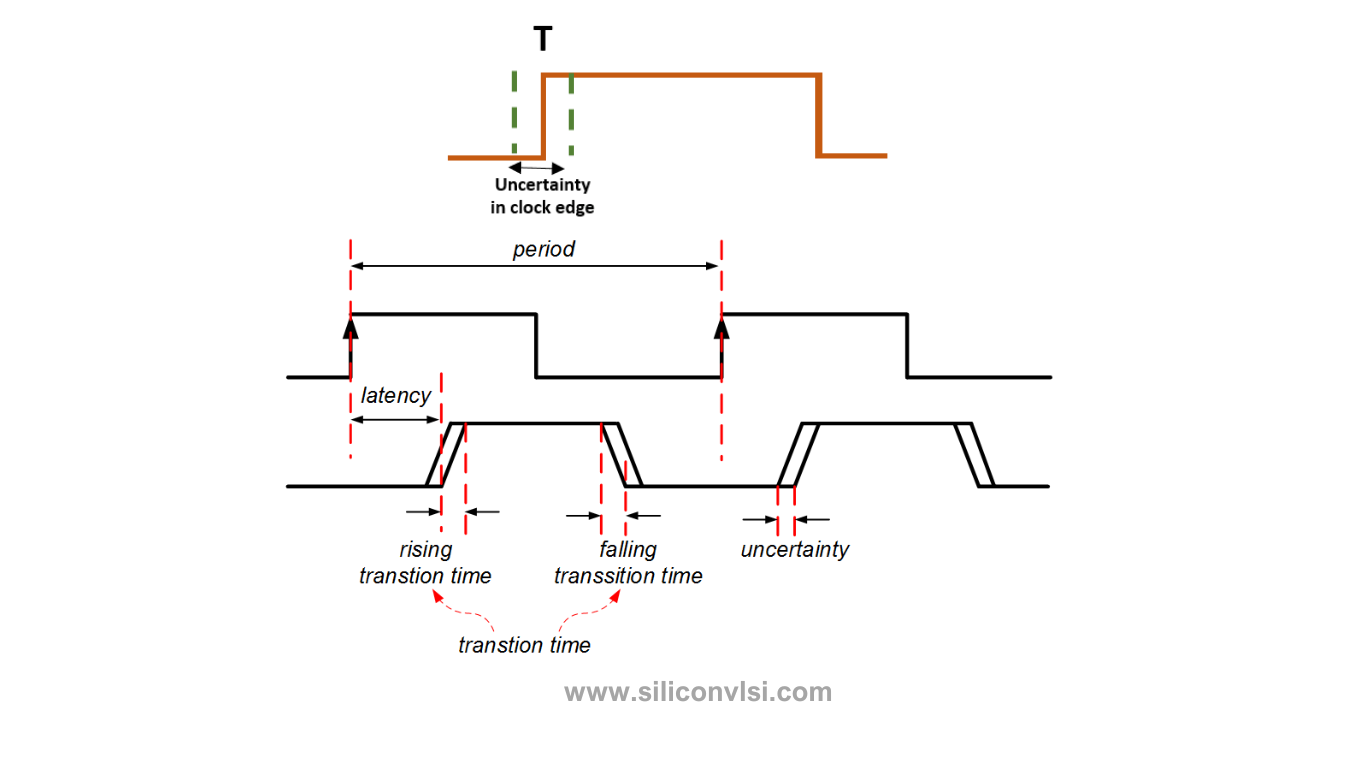
Clock skew and uncertainty are two critical factors that affect the performance and timing of integrated circuits. While they both relate to the timing aspects of a circuit, they represent different aspects of timing variation. In this section, we will explore the difference between clock skew and uncertainty in detail.
Clock Skew: Clock skew refers to the variation in arrival times of clock signals at different parts of a circuit. It occurs due to differences in path lengths, delays, and other factors that can cause one signal to reach a destination earlier or later than another signal. Clock skew can lead to timing violations and affect the proper functioning of the circuit.
Clock skew can be classified into two types: positive skew and negative skew. Positive skew occurs when the arrival times of clock signals at different points in the circuit are progressively delayed. Negative skew, on the other hand, occurs when the arrival times of clock signals are progressively advanced. Both types of skew can disrupt the synchronization between different components of the circuit.
Uncertainty: Uncertainty, also known as clock jitter or timing uncertainty, represents the variation in the timing of clock signals due to noise, interference, or other factors. It refers to the deviation or fluctuation in the actual arrival times of clock signals from their ideal or expected arrival times.
Uncertainty can arise from various sources, such as process variations, temperature variations, power supply noise, and electromagnetic interference. These factors can introduce random fluctuations in the timing of clock signals, causing uncertainty in the operation of the circuit.
Unlike clock skew, which represents a systematic variation in arrival times, uncertainty represents random variations that cannot be easily predicted or controlled. It adds an element of unpredictability to the timing behavior of the circuit.
Difference between Clock Skew and Uncertainty
The main difference between clock skew and uncertainty lies in the nature of their variations. Clock skew represents a systematic and deterministic variation in arrival times, whereas uncertainty represents a random and non-deterministic variation.
Here are a few key differences between clock skew and uncertainty:
Nature of Variation: Clock skew represents a systematic variation in the arrival times of clock signals, whereas uncertainty represents random fluctuations in timing.
Cause: Clock skew is primarily caused by differences in path lengths, delays, and other factors. Uncertainty is caused by noise, interference, process variations, and other random factors.
Effect on Timing: Clock skew can lead to timing violations and affect the synchronization between different components of the circuit. Uncertainty can introduce timing errors and increase the likelihood of setup and hold violations.
Predictability: Clock skew can be analyzed and compensated for during the design process. Uncertainty, being random in nature, is more challenging to predict and control.
Measurement and Analysis: Clock skew can be measured using techniques such as delay measurements and timing analysis. Uncertainty is typically quantified using statistical methods and analysis of timing histograms.
In summary, clock skew represents systematic variations in the arrival times of clock signals, while uncertainty represents random variations. Both factors can impact the timing and performance of integrated circuits, and designers must account for them during the physical design process.