Difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous Counter
In digital electronics, a counter is a sequential logic circuit that comprises a series of flip-flops. Counters are utilized to tally the number of occurrences of an input in terms of negative or positive edge transitions.
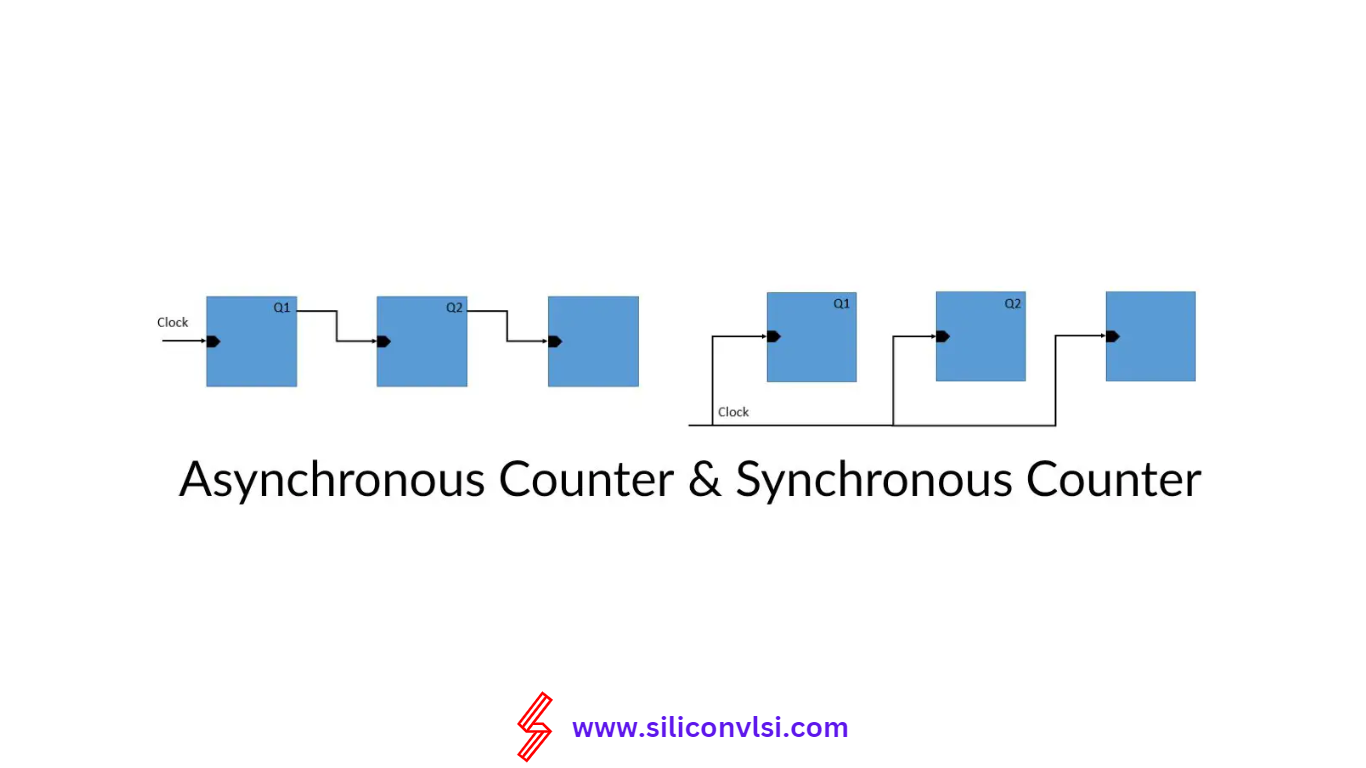
What is a Synchronous Counter?
When you look at a Synchronous Counter, you’ll notice that it’s a type of counter where clock pulses are applied to all the flip-flops simultaneously, making it what we call a parallel counter.
In this setup, each flip-flop is connected to the same external clock signal in a cascade arrangement. This design means that all flip-flops receive the clock input at the same time, so their outputs change in perfect sync with the clock pulses.
Because of this synchronized clock signal, each flip-flop changes state simultaneously, eliminating any ripple effect or propagation delay, which is a common issue in asynchronous counters. To manage the count sequence effectively, logic gates are used within the synchronous counter.
What is an Asynchronous Counter?
An Asynchronous Counter, also known as a serial counter, consists of flip-flops connected in series, with the clock pulse provided to the first flip-flop in the connection.
The output of the first flip-flop serves as the input for the next adjacent flip-flop in the forward direction, resulting in the clock input rippling through the counter. Consequently, these counters are also called ripple-counters. The ripple effect leads to a delay in the timing signal as it passes through each flip-flop, resulting in a propagation delay.
Difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters
Here are the key differences between Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters:
Synchronous Counter:
All the constituent flip-flops are triggered simultaneously with the same clock.
Operates at a faster speed compared to an asynchronous counter.
Less error-prone as each flip-flop is individually clocked.
Design and implementation are more complex.
Can be operated in any desired count sequence by manipulating the clock sequence.
No propagation delay was observed.
Asynchronous Counter:
Different flip-flops are triggered with different clocks.
Operates at a relatively slower speed compared to a synchronous counter.
More error-prone, leading to decoding errors in the system.
Design and implementation are relatively simpler.
Operates only in a fixed count sequence, i.e., UP and DOWN.
The subsequent propagation delay from one flip-flop to another.
In conclusion, a synchronous counter clocks all its flip-flops simultaneously with the same clock input, while an asynchronous counter clocks the constituent flip-flops with different signals at different time instants.