What is Flash Memory(Definition)
Flash memory, also known as flash storage, is a type of nonvolatile memory that erases data in units called blocks and rewrites data at the byte level. Flash memory is widely used for storage and data transfer in consumer devices. The first flash devices were created as an attempt to improve on the EEPROM in each of these aspects with the compromise coming in the form of the block rather than byte erasure. These flash devices are referred to as NOR flash technology.
NOR flash technology
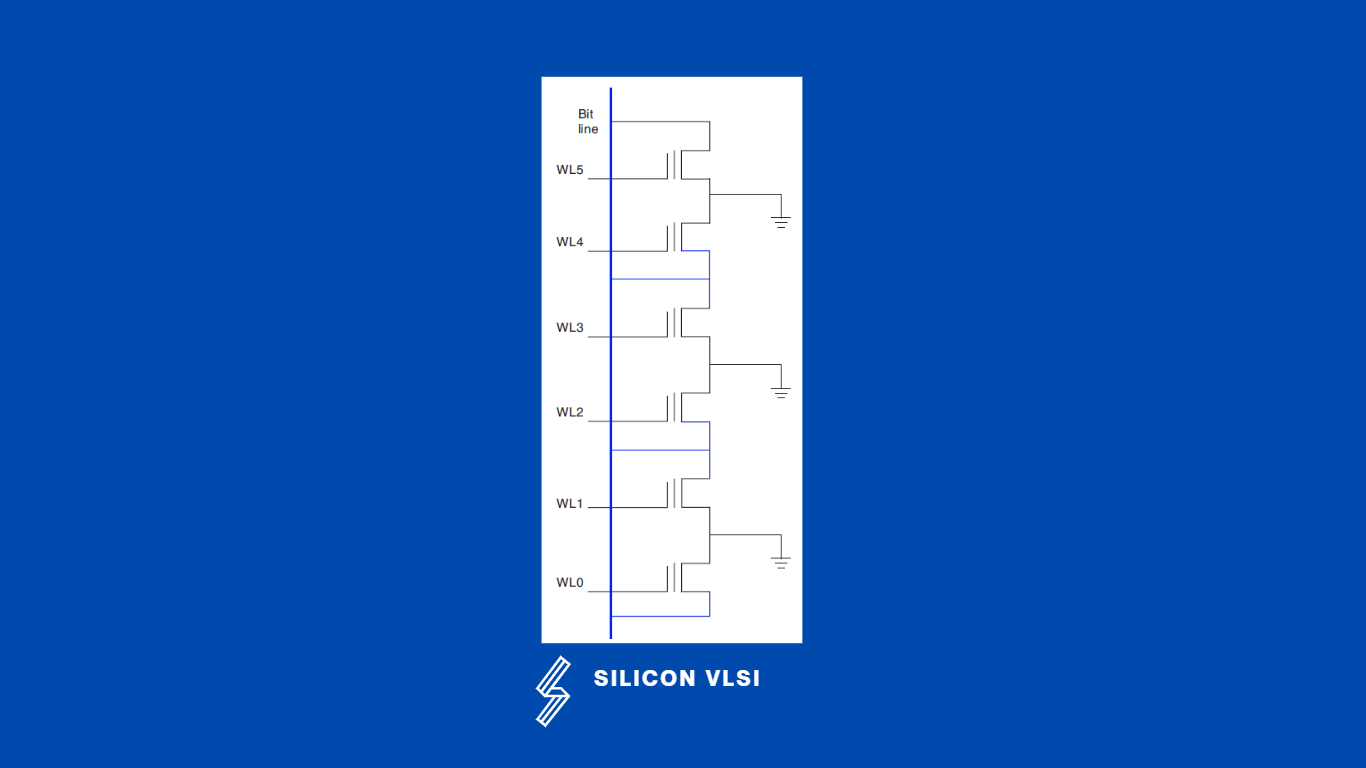
The NOR flash technology utilizes floating-gate MOSFETS (FGMOSFET) that are arranged in parallel with each other between the bit line (columns in the matrix) and ground as shown in the following figure. Notice that each word line (rows in the matrix) controls a transistor switch that can connect the bit line (column) to the ground. If WL0 OR WL1 OR WL2 . . . OR WL5 is HIGH, then the bit line will be pulled LOW. This circuit configuration functions logically like a NOR gate, which is why it is called NOR flash. Each transistor can be read or written independently of the status of the other transistors in the group. #
NAND flash technology
NAND flash memory is a type of non-volatile storage technology that does not require power to retain data. The result was NAND flash technology, which uses a group of FGMOSFETs in series with each other, connecting the bit line with the ground as shown in the following figure. Notice that to get the bit line pulled LOW requires the activation (HIGH) of WL0 AND WL1 AND WL2 . . . AND WL7, which is like the logical function of a NAND gate, hence the name NAND flash. For the NAND flash circuit, the data stored on each transistor must be accessed in conjunction with the other word lines in its group being activated by a control gate, a voltage large enough to turn on other transistors regardless of the amount of charge on the floating gate.
For example, to read the data on the transistor connected to WL1, a normal control voltage is applied to WL1, which causes its MOSFET to turn on if logic 0 is stored on it or remain off if logic 1 is stored. At the same time, the other transistors are forced on by a higher voltage on their word lines (WL0, WL2–WL7), which assures that they form a low resistance path and effectively allows the data stored on the MOSFET of WL1 to control the voltage on the bit line. #
![]()
NAND flash technology
Where does the term flash memory come from?
Masuoka’s colleague, Shoji Ariizumi, reportedly coined the term flash because the process of erasing all the data from a semiconductor chip reminded him of the flash of a camera. Flash memory is credited to having been created by Fujio Masuoka while he was working for Toshiba in the 1980s. #
What is the function of a flash memory’s command register?
The FLASH Commands register (FCMD) is located at $1826. The flash memory’s command register supports, #
- Blank Check,
- Byte Program,
- Byte Burst Program,
- Page Erase, and
- Mass Erase.
Which flash configuration is byte erasable?
Flash memory can be electrically erased and reprogrammed and it erases data in units called blocks and rewrites data at the byte level. #
What is the main advantage of flash memory over EEPROMs?
Flash is erasable in blocks, but EEPROM is erasable in bytes. While other EEPROMs are rarely rebuilt, flash is constantly updated. When significant volumes are required, flash is employed, but EEPROM is only used sometimes. EEPROM has more longevity than flash. #
Which flash configuration is used in USB thumb drives?
A USB flash drive also called a thumb drive, jump drive, pen drive and USB memory stick is a device that can be used to save information on a tiny flash memory. Most USB flash drives will have a FAT32 file system out of the box. It is the most compatible file system for older/modern computers. #
Advantages of Flash Memory
- Less prone to damage. #
- Small size, portability.
- High transferring speed.
- Large and increased capacity.
- Work more quietly than the physical hard drive.
- Low power consumption than traditional hard disk drives.
Disadvantages of Flash Memory
- Writing (1->0) is expensive. #
- Erasing (0->1) is super expensive.
- High price compared to hard disks.
- Easy to lose due to its smaller size
- The Limited number of reads/writes before failing.
Conclusion
The flash technologies NAND and NOR both have benefits and drawbacks. Although the NAND memory circuit allows for a quick program and erases time, the data must be handled in blocks. Faster read access times and random access are provided by NOR Flash. As a result, NAND flash is typically used for mass storage of images, music, and other files in gadgets like digital cameras, memory cards, and USB flash drives, while NOR flash is typically used for things like BIOS chips for your computer. As with other rapidly developing technologies, methods are being developed to benefit from NAND flash’s increased density and cheaper cost per bit while emulating its performance in an increasing number of applications.
