What is the full form of LED?
LED fill form is Light Emitting Diodes, which are revolutionary semiconductor devices that emit captivating light when an electric current passes through them. These small yet powerful components have transformed the lighting industry and found extensive use in a myriad of applications. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the working principle behind LEDs, explore different types, and uncover the vast array of applications where these remarkable devices shine brightly.
Understanding the Symbol of LED
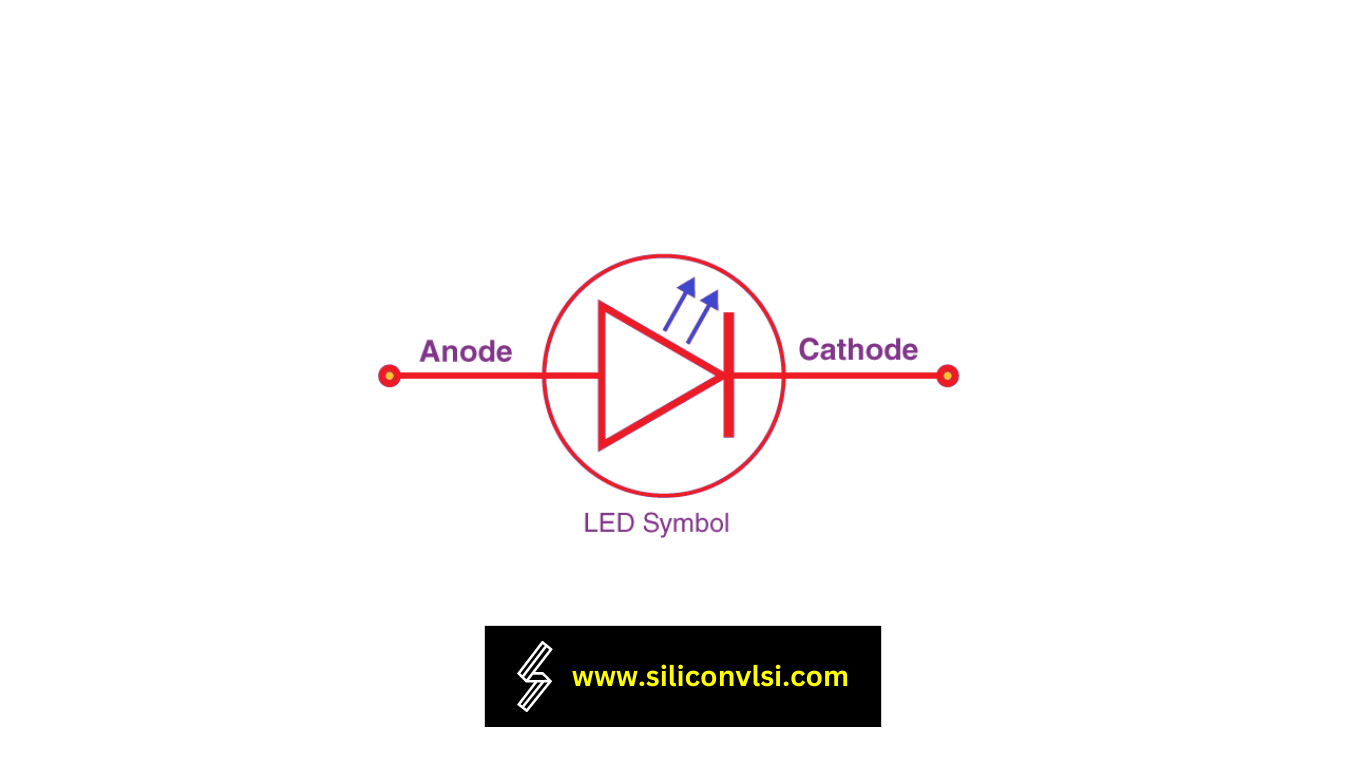
The symbol of an LED bears a striking resemblance to that of a p-n junction diode. However, a key distinction lies in the presence of two arrows that signify the emission of light, as illustrated above. This symbolic representation captures the essence of how LEDs illuminate our world with their radiant glow.
Unveiling the Working Principle of LEDs
At the core of LED technology lies the synergy between two types of semiconductors: a type P semiconductor, rich in positively charged holes, and a type N semiconductor, abundant in negatively charged electrons. When a suitable forward voltage is applied across the P-N junction, a fascinating phenomenon takes place. Electrons and holes recombine, unleashing energy in the form of light. This captivating process fuels the brilliance of LEDs and allows them to illuminate our surroundings with efficiency and elegance.

Exploring the Different Types of LEDs
LED technology has evolved to encompass a wide range of specialized types, each designed to cater to specific applications. Let’s take a closer look at some prominent categories:
Miniature LEDs: These compact LEDs find widespread use in various electronic devices, from indicators on circuit boards to handheld gadgets. Their small size and energy efficiency make them a popular choice in portable electronics.
Lighting LEDs: With their exceptional brightness and long lifespan, lighting LEDs have revolutionized the lighting industry. They offer energy-efficient alternatives to traditional incandescent bulbs, allowing for vibrant and sustainable illumination in homes, offices, and public spaces.
Red Green Blue LEDs: RGB LEDs combine the primary colors of red, green, and blue to create a vast spectrum of hues. These versatile LEDs are extensively employed in decorative lighting, signage, displays, and even theatrical productions, where vibrant and dynamic lighting effects are desired.
Flash LEDs: Flash LEDs, also known as camera flash modules, play an important role in photography. These high-intensity LEDs provide the necessary burst of light to capture clear and well-exposed images, even in low-light conditions.
High-Power LEDs: Designed to emit intense luminosity, high-power LEDs are the workhorses of modern lighting applications. They find extensive use in outdoor lighting, automotive headlights, stadium displays, and architectural lighting, among many others.
Alphanumeric LEDs: Alphanumeric LEDs are specifically designed to display numbers, letters, and symbols. They are commonly utilized in digital signage, scoreboard displays, and alphanumeric indicators, providing clear and legible information in a compact format.
LED Applications
The extraordinary capabilities of LEDs have made them indispensable across a diverse range of industries and fields. Let’s explore some of the notable applications where LEDs shine brightly:
Various Displays: LEDs have revolutionized the display industry, from large-scale video walls to tiny screens on smartphones. Their compact size, energy efficiency, and vibrant color reproduction have enabled the creation of stunning visual experiences in advertising, entertainment, and information dissemination.
Dimming of Light: LEDs are widely employed in dimmable lighting fixtures, allowing users to adjust brightness levels according to their preferences. This versatility is especially valuable in homes, hotels, restaurants, and other environments where creating the desired ambiance is important.
Automotive Industry: LEDs have illuminated the automotive industry
with their advanced lighting solutions. From headlights and taillights to interior and dashboard lighting, LEDs offer enhanced visibility, energy efficiency, and longevity, contributing to improved safety on the road.
TV Backlighting: The television industry has embraced LED backlighting technology, enabling slimmer designs, better contrast ratios, and energy-efficient performance. LED-backlit TVs provide viewers with vibrant, lifelike visuals, enhancing the overall viewing experience.
Specialty Lighting: LEDs find application in specialty lighting, including underwater illumination, horticultural lighting for plant growth, and architectural accent lighting to highlight the unique features of buildings and structures. Their versatility and precision make them ideal for creating captivating lighting effects in various contexts.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored the captivating world of LEDs, we’ve witnessed their incredible working principle, discovered diverse types that cater to specific needs, and uncovered a myriad of applications where they illuminate our lives. These semiconductor marvels continue to shape the lighting landscape and redefine what is possible in terms of efficiency, versatility, and visual impact. With their radiant glow, LEDs will undoubtedly continue to shine brightly, lighting the way to a brighter and more sustainable future.