The MOSFET, in combination with other circuit elements, can be utilized to amplify small time-varying signals. Figure 1, depicts the MOSFET small-signal amplifier, which is a common-source circuit where a time-varying signal is coupled to the gate using a coupling capacitor. In Figure 1, the transistor characteristics and the load line are shown. The load line is determined when vi (input voltage) is equal to 0.
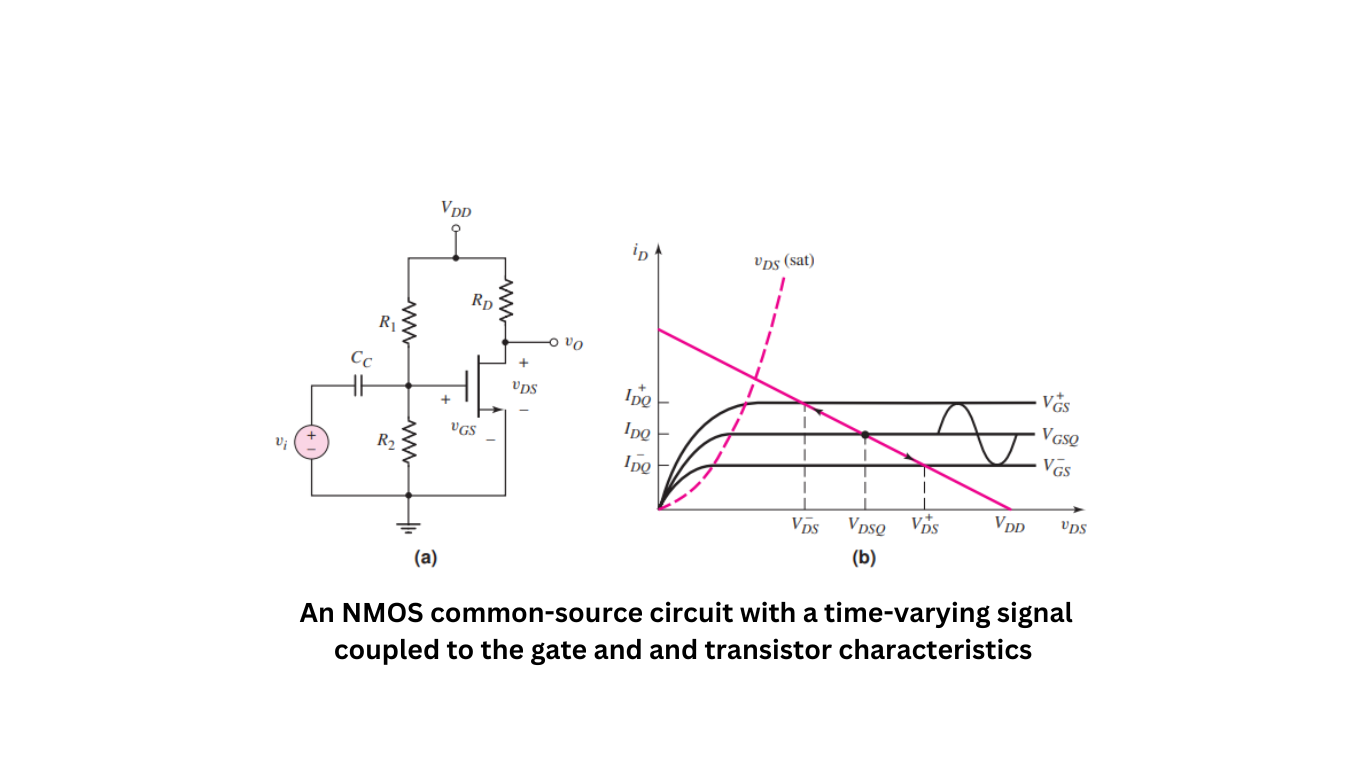
To establish a specific Q-point on the load line, the ratio of the bias resistors R1 and R2 can be designed accordingly. If we assume that vi = Vi * sin(ωt), the gate-to-source voltage will have a sinusoidal signal superimposed on its dc quiescent value. As the gate-to-source voltage changes over time, the Q-point will move along the load line, as indicated in the figure.
This movement along the load line results in a sinusoidal variation in both the drain current and the drain-to-source voltage. As a consequence, the variation in the output voltage can be larger than the input signal voltage, indicating that the input signal is amplified. The actual signal gain depends on both the transistor parameters and the values of the circuit elements.
