Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) relies on the digitization of audio signals, allocating a single frequency channel for a short period before moving to another channel. Time slots are used to divide the radio spectrum, and in each slot, only one user is allowed to transmit or receive. Each user occupies a cyclically repeating time slot, forming a frame.
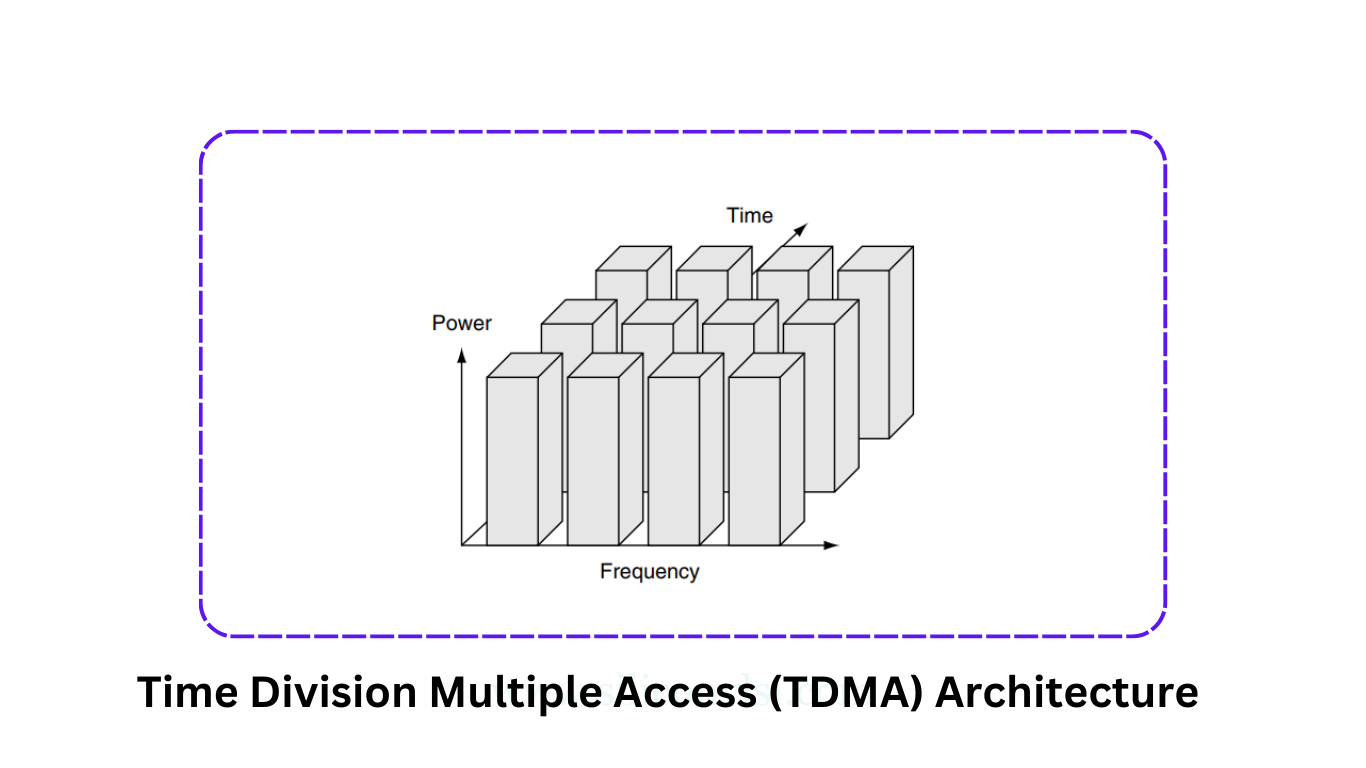
In TDMA, the transmission from various users is interlaced into a repeating frame structure, consisting of a preamble, information bits, and trail bits. Guard times are used between each user’s transmission to minimize crosstalk.
Advantages of TDMA
- Flexible Bit Rate:
- TDMA allows a flexible bit rate for multiples or submultiples of a basic single-channel rate, accommodating various traffic types.
- Simpler Handoff Process:
- Handoff processes in TDMA are simpler for subscriber units as they can listen for other base stations during idle time slots.
- Integration into VLSI:
- TDMA potentially integrates into Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) without narrow-band filters, leading to a low-cost floor in volume production.
- Duplexer Elimination:
- TDMA uses different time slots for transmission and reception, eliminating the need for duplexers.
- Dynamic Time Slot Allocation:
- Different numbers of time slots per frame can be allocated to different users, allowing dynamic bandwidth allocation based on priority.
- Adaptability to Data Transmission:
- TDMA can easily adapt to the transmission of data as well as voice communication.
- Versatility in Data Rates:
- TDMA offers the ability to carry data rates from 64 kbps to 120 Mbps, enabling various services, including multimedia and video conferencing.
- Interference Avoidance:
- TDMA’s time-based separation ensures that users on the same frequency band will not experience interference from other simultaneous transmissions.
- Extended Battery Life:
- Users experience extended battery life and talk time as the mobile is transmitting only a portion of the time during conversations.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency:
- TDMA installations offer cost savings in base station equipment, space, and maintenance, making it a cost-effective technology for upgrading analog systems to digital.
- Compatibility and Efficient Use of Cell Structures:
- TDMA is inherently compatible with FDMA analog systems, allowing efficient use of hierarchical cell structures (HCSs) and supporting pico, micro, and macrocells.
Disadvantages of TDMA
- Signal Processing Requirements:
- TDMA requires substantial signal processing for matched filtering and correlation detection for synchronization with a time slot.
- Potential Call Disconnection:
- Users roaming from one cell to another without allotted time slots may face disconnection if all time slots in the next cell are occupied.
- Multipath Distortion:
- TDMA is susceptible to multipath distortion, where signals arriving from different directions may lead to distortion.
In summary, TDMA offers numerous advantages, including flexibility, simplicity in handoff, integration capabilities, dynamic allocation, adaptability to data transmission, versatility in data rates, interference avoidance, extended battery life, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility. However, challenges include signal processing requirements, potential call disconnection during roaming, and susceptibility to multipath distortion