Fermi Level
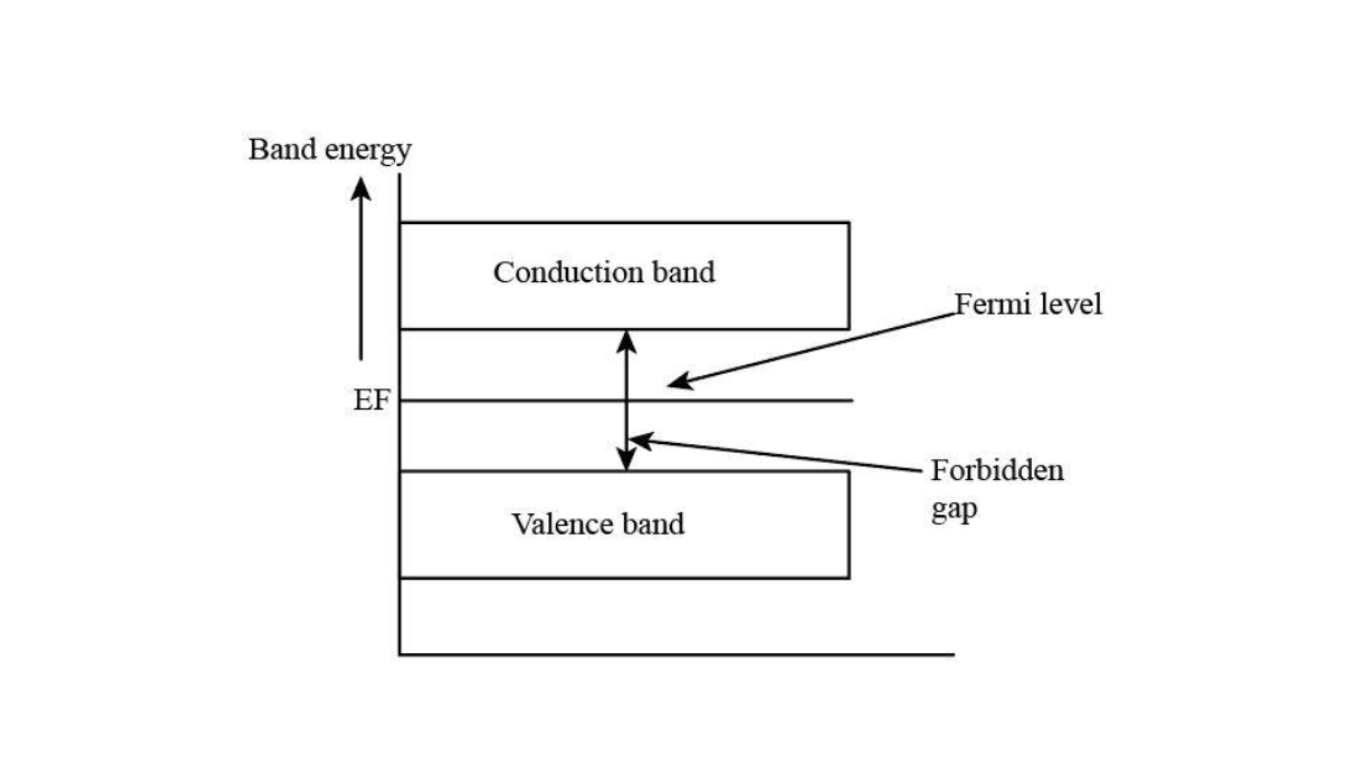
The Fermi Level is the maximum energy level an electron may occupy when it is at absolute zero degrees Fahrenheit. Since the electrons are all in the lowest energy state at absolute zero, the Fermi level is located between the valence band and conduction band.
Fermi Energy Level
The energy of the Fermi level divided by the Boltzmann constant is known as the Fermi temperature. Additionally, it is the temperature at which the electron’s energy equals the Fermi energy. It is a measurement of the metal’s electrons in their lower energy states.
Pauli’s exclusion principle, which stipulates that two fermions cannot occupy the same quantum state, is what causes this energy level to exist. Therefore, if a system contains many fermions, each fermion is associated with a unique set of magnetic quantum numbers.
Applications of Fermi Energy
It is used in insulators and semiconductors.
It is used to describe metals, semiconductors, and insulators.
The electrical and thermal properties of the solids are assessed using Fermi energy.
Fact about Fermi Level
The Fermi energy level changes when a forward bias is applied; for the n-type, it rises, whereas for the p-type, it falls.
The Fermi energy level will rise for the p-type when a reverse bias is applied, but it will fall for the n-type.
Fermi energy level decreases for n-type, and for p-type, and it increases until equilibrium is obtained.