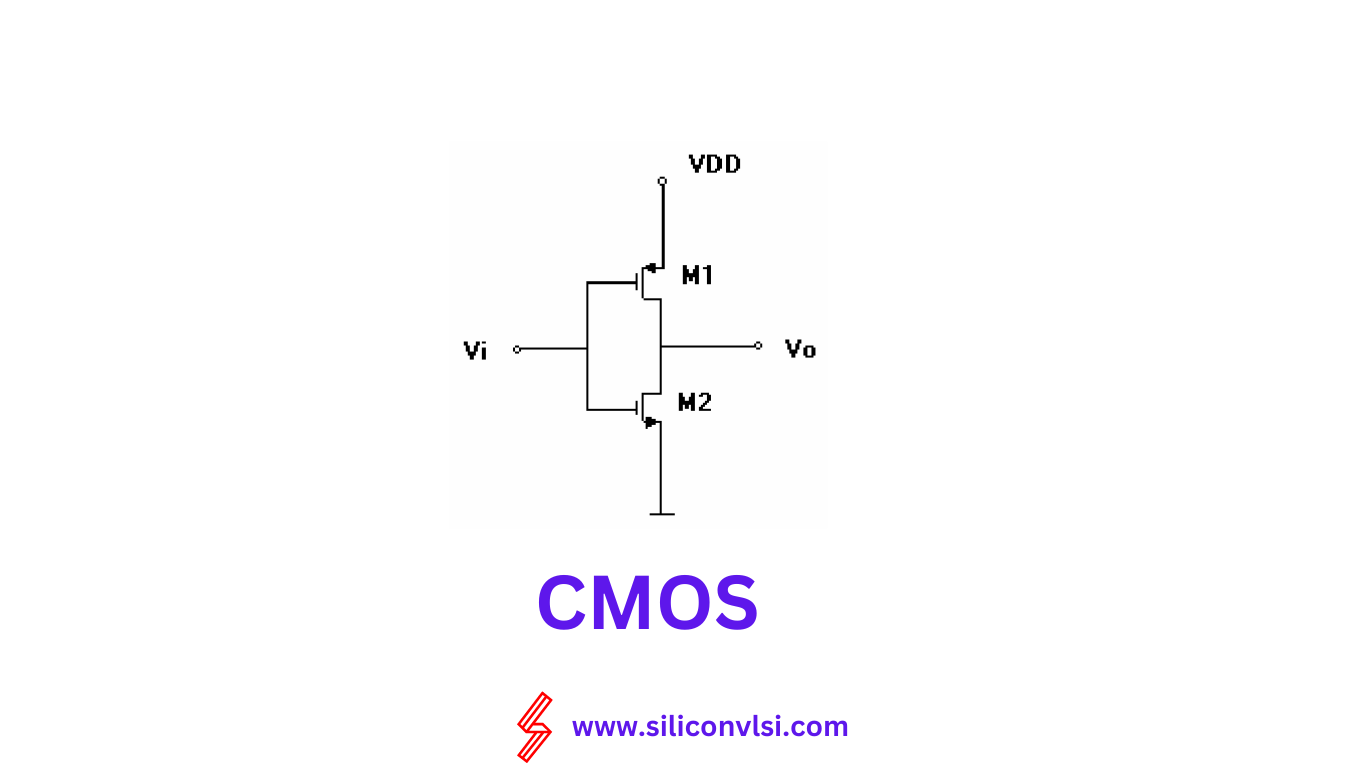
CMOS stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, while NMOS stands for N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor. These are two types of logic families used in electronic circuits. CMOS uses both PMOS and MOS transistors while NMOS only uses FETs.
CMOS is preferred over NMOS for designing embedded systems because it can handle both logic 0 and 1, while NMOS can only handle logic 1 (VDD). In NMOS, the output voltage after passing through the gate is VDD-Vt. On the other hand, CMOS technology is chosen because it can propagate both logic 0 and 1 effectively.
In CMOS logic gates, a combination of n-type MOSFETs and p-type MOSFETs is used. The n-type MOSFETs create a pull-down network between the low-voltage power supply rail and the output, while the p-type MOSFETs form a pull-up network between the high-voltage rail and the output. When the gates of both types of transistors are connected to the same input, the p-type MOSFET will be on when the n-type MOSFET is off, and vice versa.
Both CMOS and NMOS technologies are used in digital logic circuits, static RAM, microprocessors, data converters, image sensors, and other electronic devices. However, CMOS technology is preferred over NMOS due to its superior features such as low static power consumption, resistance to noise, energy efficiency, and absence of heat generation. Though CMOS technology may be more expensive, its complex composition makes it difficult for unauthorized production.
In conclusion, CMOS technology is highly suitable for designing embedded systems due to its advantages. If you have any further questions or need a better understanding, please feel free to ask.
