Capacitors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, widely used for energy storage, filtering, and voltage regulation. Among various types of capacitors, MOM, MIM, and MOS capacitors stand out due to their unique properties and applications. Understanding the differences between these capacitor types is crucial for choosing the right one for your electronic design needs.
In analog IC circuit design, capacitors are essential components. Traditionally, metal capacitors have been widely used in integrated circuits. In CMOS technology, there are three main types of integrated capacitors:
- MIM capacitors (Metal-Insulator-Metal)
- MOM capacitors (Metal-Oxide-Metal)
- MOS capacitors (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
Each of these capacitor types serves different purposes and offers distinct advantages and disadvantages.
MIM Capacitor (Metal-Insulator-Metal)
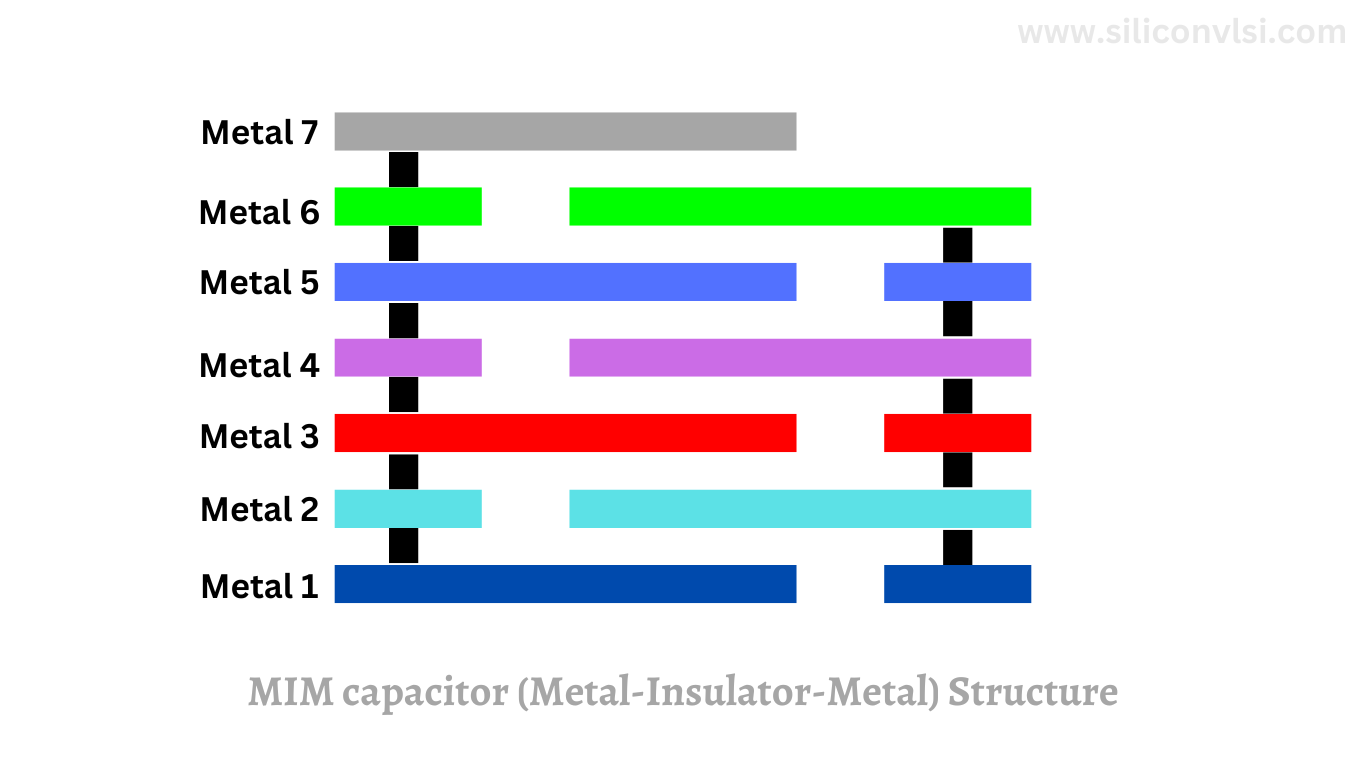
MIM, or Metal-Insulator-Metal capacitors, consist of a dielectric layer sandwiched between two metal layers. This design provides a significant advantage in terms of miniaturization, making MIM capacitors ideal for compact electronic devices like smartphones and tablets. Furthermore, MIM capacitors deliver exceptional charge storage capabilities, allowing for rapid discharge and fast switching, which is essential in high-speed applications.
MOM Capacitor (Metal-Oxide-Metal)
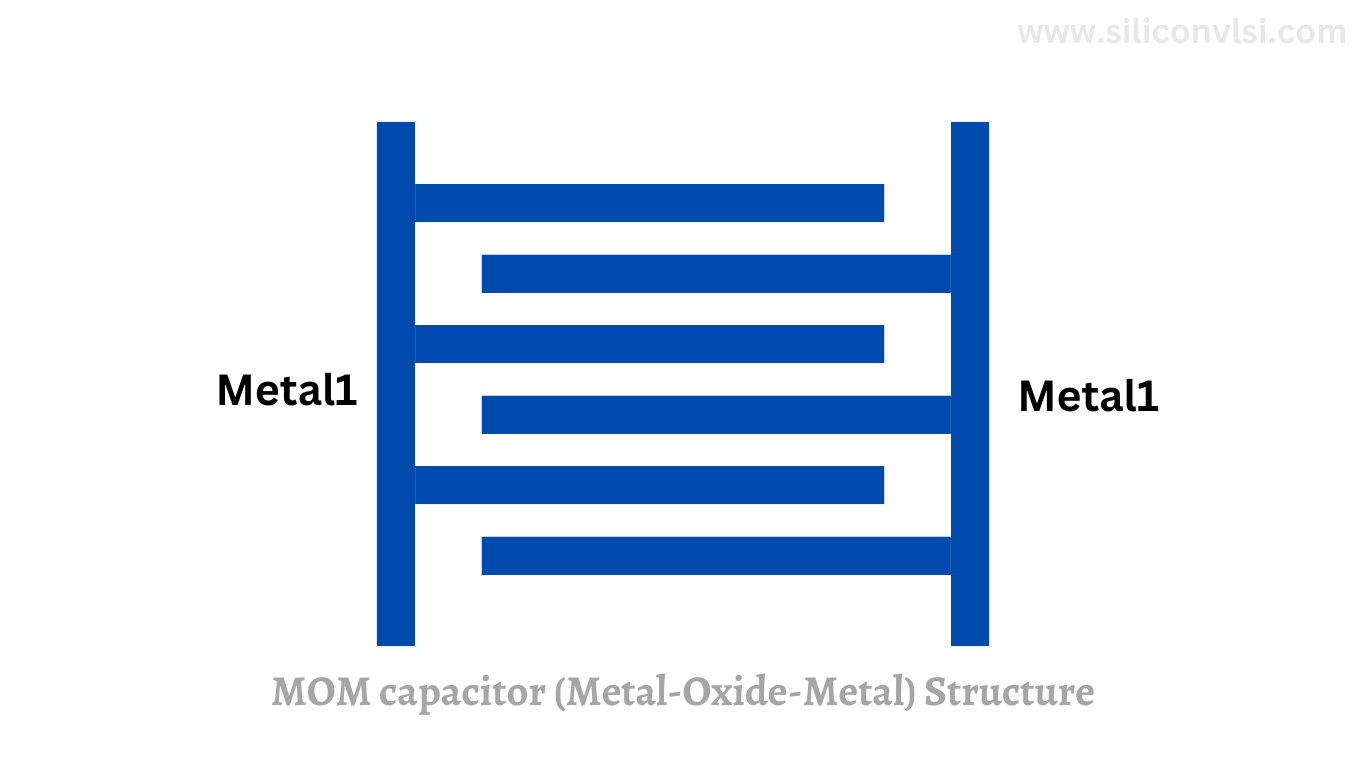
MOM, or Metal-Organic-Metal capacitors, are typically made of a metal substrate coated with organic materials. The structure of MOM capacitors allows them to exhibit excellent capacitance stability and high frequency performance. These capacitors are often employed in RF applications where size and efficiency are critical. The ability to handle high temperatures also makes MOM capacitors suitable for automotive or industrial environments.
MOS Capacitor (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
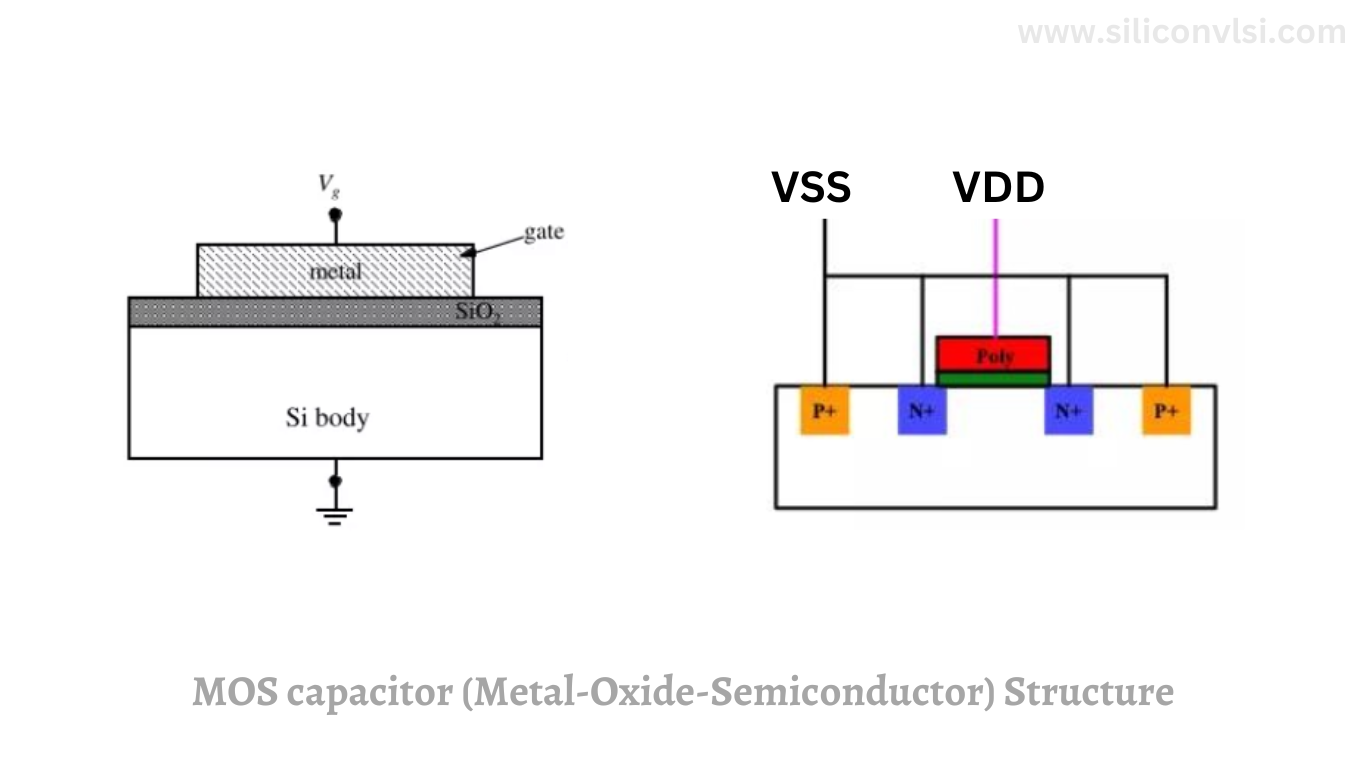
MOS, or Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor capacitors, integrate oxide insulators, offering good voltage handling and low leakage currents. With their robust construction, MOS capacitors are often found in analogue and digital circuits alike. They are particularly useful in power management systems, where maintaining stability is essential.
In summary, while MOM, MIM, and MOS capacitors serve similar functions in electronic devices, their distinct structures and characteristics suit them for different applications. By understanding their differences, engineers can effectively select the appropriate capacitor type to meet specific project requirements.
Comparison of Capacitors
MIM capacitors are similar to plate capacitors, offering accurate capacitance values that do not change with bias voltage. They are suitable for analog and RF processes.
MOM capacitors use interdigital structures and have good capacitance density but may lack determinism and stability compared to MIM capacitors. They are used in processes that do not require high capacitance.
MOS capacitors are voltage-controlled capacitors used within MOSFETs. They exhibit non-linearity and vary their capacitance with gate voltage. They are not suitable for circuits requiring high precision but are essential in transistor operation.
In summary, the choice between MIM, MOM, and MOS capacitors depends on the specific requirements of the circuit and the technology being used. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications in CMOS technology. MOM capacitors have gained prominence in advanced manufacturing processes due to their high unit capacitance and low parasitic capacitance.