What is a Linear Feedback Shift Register?
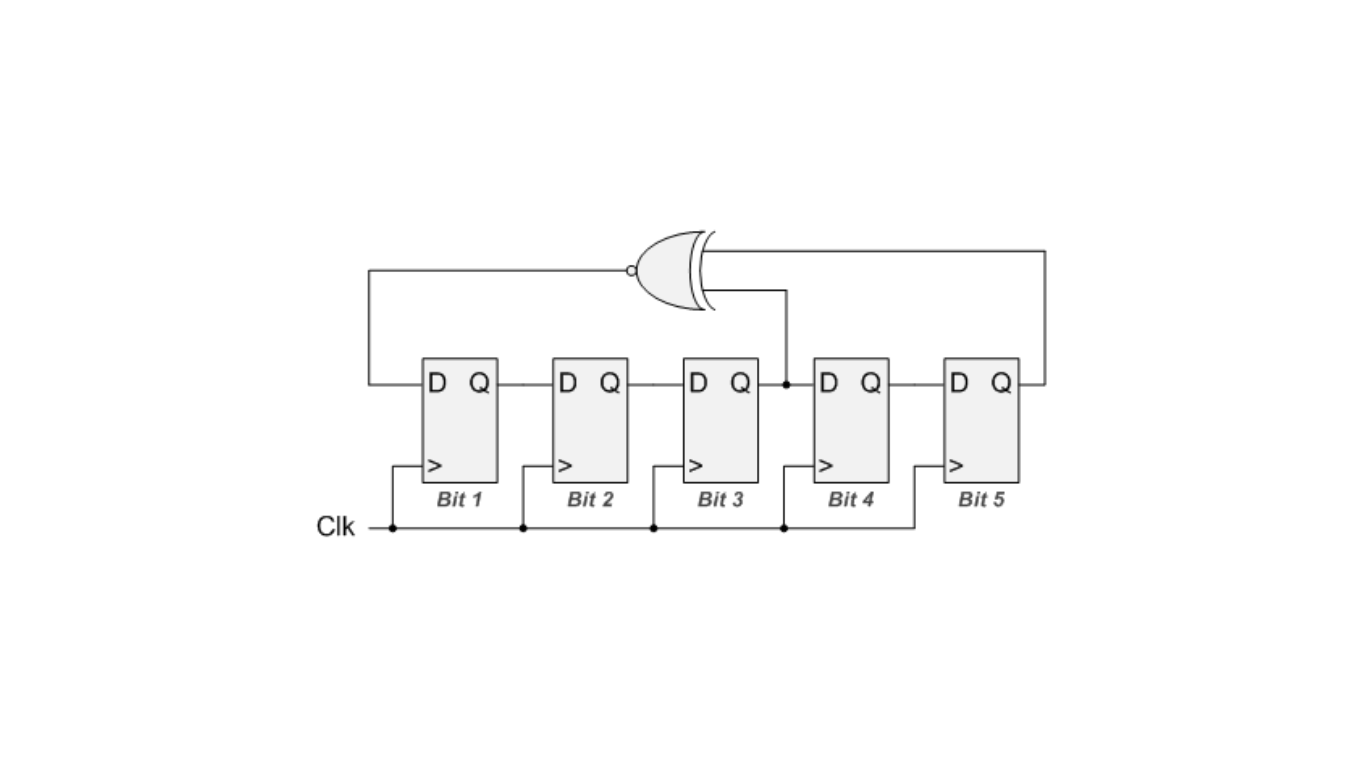
In a linear feedback shift register (LFSR), carry generation plays a crucial role. An LFSR is a type of shift register used for various purposes, including generating pseudo-random patterns and compressing responses in Built-In Self-Test (BIST) systems.
Here’s how to carry generation works in an LFSR
Initial State
The LFSR begins with an initial state, which consists of values stored in its flip-flops (memory cells). This initial state determines the sequence of bits the LFSR will generate.
Clock Synchronization
The flip-flops in the LFSR are synchronized by a common clock signal, ensuring that they change values at the same time.
Feedback Mechanism
The core of carry generation is the feedback mechanism. In this mechanism, the values in the flip-flops are processed using XOR operations (modulo-2 addition). The XOR network computes new values based on the current state and feedback values. These new values are then shifted into the flip-flops.
Sequence Generation
As the LFSR shifts bits and computes new values through feedback, it generates a sequence of bits over time. This sequence depends on the initial state and the specific feedback polynomial used.
Repetition
LFSRs are designed to generate sequences that repeat after a certain number of clock cycles. The length of this sequence is determined by the number of flip-flops in the LFSR and the feedback polynomial.
What is Carry Generation?
Carry Generation refers to the process by which the register generates and propagates values or bits within itself. In particular, it involves the generation of new bits based on the current state of the register and its previous values, often involving mathematical operations like addition or exclusive-OR (XOR).
The key idea is that an LFSR can autonomously generate a sequence of bits that appears random but is entirely determined by its initial state and feedback polynomial. The carry generation process is what allows it to create this sequence efficiently.