Why PMOS pass strong 1 and weak 0
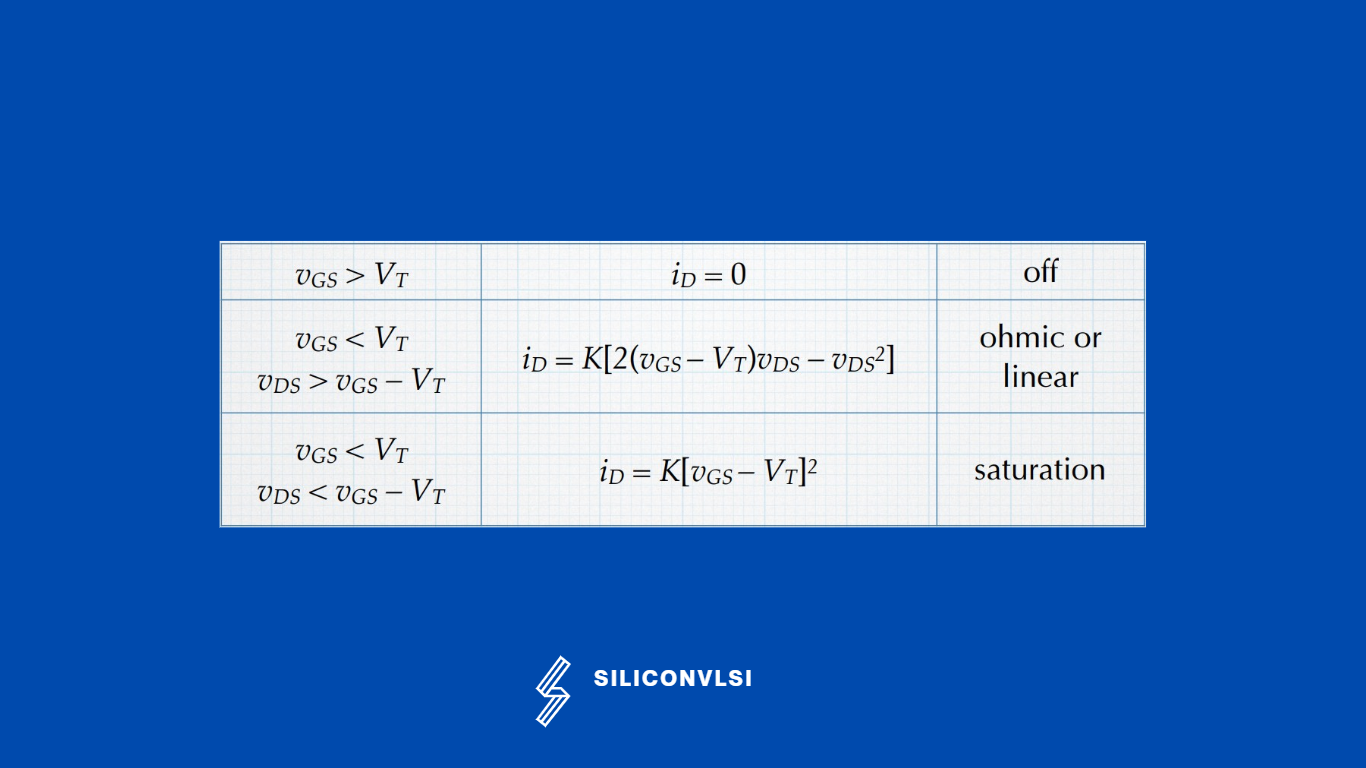
The current equation for PMOS is the following, for PMOS to turn on, Vgs should be less than Vt.
The current equation for PMOS
Now to understand PMOS pass strong 1 and weak 0, let’s take one example. Suppose we have one PMOS. As shown in the following figure, let’s take Vcc =1v, Vg = 0, and Threshold voltage(Vt) = – 0.2v. And Initially, Capacitor(Vcc) is 1v. And drain terminal is tied to ground
![]()
After some time, As shown in the following figure, after discharge, Vcc node is 0.8v, Vg = 0 and Threshold voltage(Vt) = – 0.2v.
So Vgs = Vg – Vs = 0 – 0.8 = -0.8 < -0.2. This means still Vgs < Vt condition is satisfying.
![]()
After some time, As shown in the following figure, after some more discharge, Vcc node is 0.4v, Vg = 0 and Threshold voltage(Vt) = – 0.2v. So Vgs = Vg – Vs = 0 – 0.4= -0.4< -0.2. This means still Vgs < Vt condition is satisfying.
![]()
After some time, As shown in the following figure, after some more discharge, Vcc node is 0.2v, Vg = 0 and Threshold voltage(Vt) = – 0.2v. So Vgs = Vg – Vs = 0 – 0.2= -0.2 = -0.2. This means still Vgs < Vt condition is satisfying.
![]()
Now we reach a critical point of PMOS, now after that, this Vcc cap will not discharge further because Vg -Vs < Vt condition will no more satisfying. So based on the above example, we can say that PMOS passes weak Zero. This means in the above example, the capacitor will not be discharged fully.
pMOS Pass Characteristics
![]()
What is the meaning of strong 1 and strong 0?
In digital circuitry, when we refer to a “strong 1” or a “strong 0,” we mean that the output signal is capable of strongly driving either a high voltage (Vdd) or a low voltage (ground, GND), respectively.
For an NMOS (N-type Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) transistor to be turned ON and allow the passage of a high signal (logic 1), its gate should be supplied with a voltage equal to Vdd.
Conversely, for a PMOS (P-type Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) transistor to be turned ON and allow the passage of a low signal (logic 0), its gate should be connected to the ground (GND).
This distinction ensures that the transistors in the circuit behave appropriately to produce the desired logic levels at the output.
Please comment below if You like this article.