Double Patterning
To get better resolution and get higher density, double patterning is used. For the following nodes, only the 193 nm water-based immersion lithography is a possibility. However, with a maximum practical NA of 1.35, its resolution limit is somewhere between 40 and 50 nm. Double patterning has become the semiconductor industry’s preferred technique in this case. There are three main double pattern techniques are there. LELE, LFLE, and SADP. let’s see it in detail.
LELE(Litho-Etch-Litho-Etch)
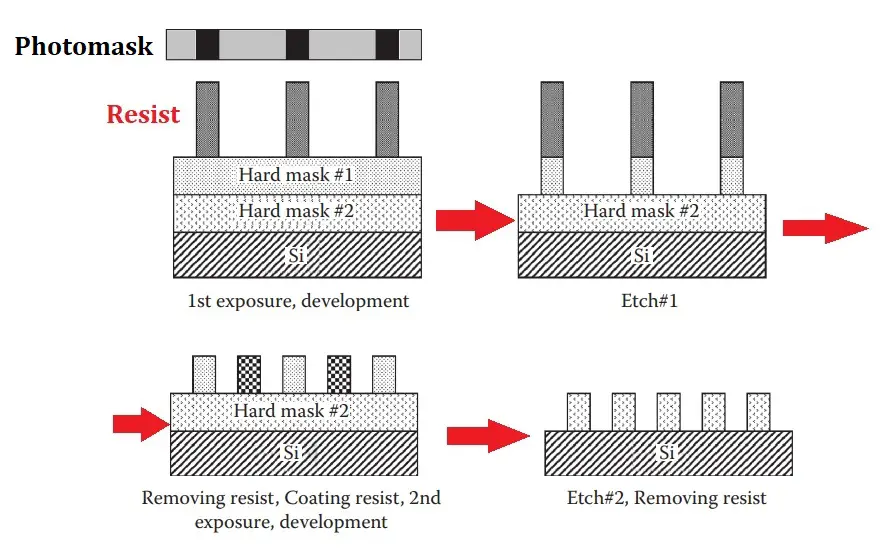
#In litho-etch-litho-etch (LELE), a type of double patterning, features are printed at a relaxed pitch that is compatible with 193 nm limitation lithography, such as line and space patterns at a 1:3 critical dimension pitch ratio.
The following figure illustrates a LELE process schematic for double patterning. After resist stripping and etch transfer into the substrate, a second resist is applied, and a subsequent exposure creates a 1:3 pattern that intercalates a new line into the dense line pattern with a resolution that is not possible with direct exposure.
The LELE process requires double-etching processes. Therefore, complicated processes and higher costs are required for LELE.In theory, arbitrary patterns can be subjected to the LELE approach by being appropriately split into mask levels. Although the LELE method has been shown to be effective in real-world settings, it has the drawback of doubling the cost of patterning for the important layers.
Another drawback is how overlay mistakes affect space CDs; as demonstrated in Figure, overlay faults directly convert into CD errors. Future exposure tools’ overlay accuracy will be put under a lot more pressure because of this. This problem might be avoided with self-aligned spacers for double patterning.
Advantages of LELE(Litho-Etch-Litho-Etch)
- Provide greater resolution#
- Straightforward process
Disadvantages of LELE(Litho-Etch-Litho-Etch)
- Expensive#
- Low throughput
- Its Requires 5 process steps
- Suffer from mask misalignment
- Small tolerance for pattern overlay
LFLE(Litho-Freeze-Litho-Etch)
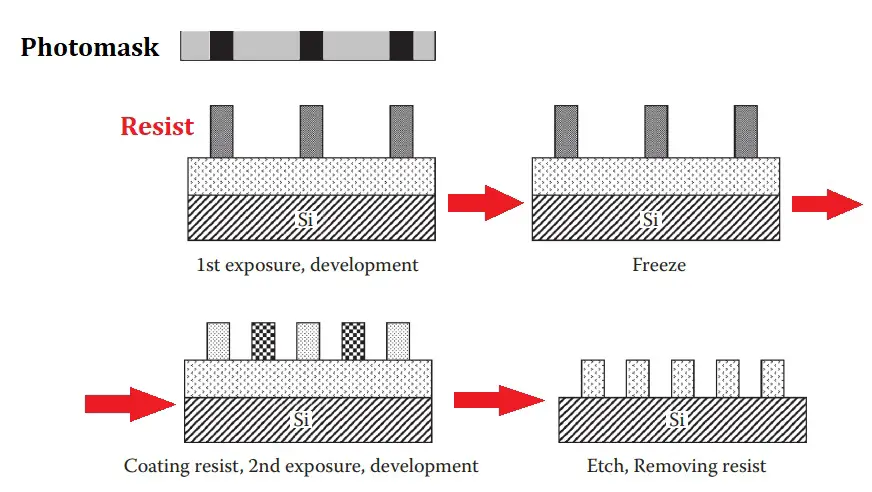
The litho-freeze method uses a tracking technique to freeze the resist before applying a second resist coat and being exposed. It only calls for one etch phase. The initial exposed/developed resist is chemically modified during the freeze, so it is not negatively impacted by later lithography operations.
The litho-freeze process, also known as LFP, is what causes this. For LFP, just one etching step is required. It is also possible to incorporate the freezing ability within the resist itself, for example, by including bake step crosslinking functionality.#
Advantages of LFLE(Litho-Freeze-Litho-Etch)
- Its needs four process steps. #
- Reduced cost.
- Increased throughput.
Disadvantages of LFLE(Litho-Freeze-Litho-Etch)
- Expensive#
- Low throughput
Self-Aligned Double-Patterning (SADP)
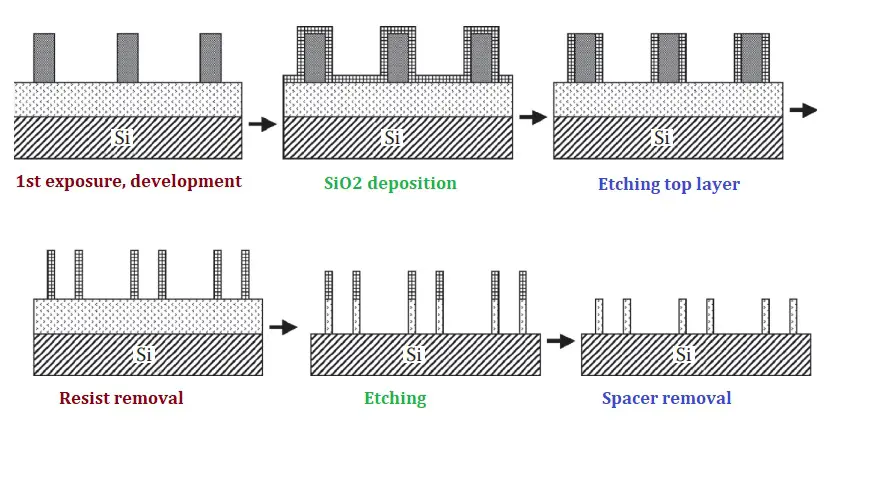
The self-aligned double-patterning (SADP) procedure is a different type of double-patterning lithography (DPL). The resist pattern serves as the core of the SADP process, as depicted in the following diagram. After the resist is exposed, developed, and masking material is applied and etched too and from sidewall spacers, the resist is finally removed.
The substrate is next etched utilizing the residual spacers as a mask once the resist material from the exposure phase has been removed. The remaining spacers are then eliminated, leaving the finished pattern.
The SADP approach has the advantages of only requiring one important exposure and having no concerns with overlay. It has been demonstrated that compared to any traditional lithography method, critical dimension uniformities (CDUs) and line edge roughness (LER)/line width roughness (LWR) is improved. #
Advantages of self-aligned double-patterning (SADP)
- No mask Misalignment #
- Increased throughput.
- Better accuracy.
Disadvantages of self-aligned double-patterning (SADP)
- Expensive#
- Require more step