Drain Induced Barrier Lowering (DIBL)
“Drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL) effect which causes a reduction in the threshold voltage as the channel length decreases”
DIBL(Drain induced barrier lowering) effect occurs when the barrier height for channel carriers at the edge of the source reduces due to the influence of the drain electric field, upon application of a high drain voltage. This increases the number of carriers injected into the channel from the source leading to an increased drain offcurrent. DIBL(Drain induced barrier lowering) effect is also called Shortchannel effects (SCE).
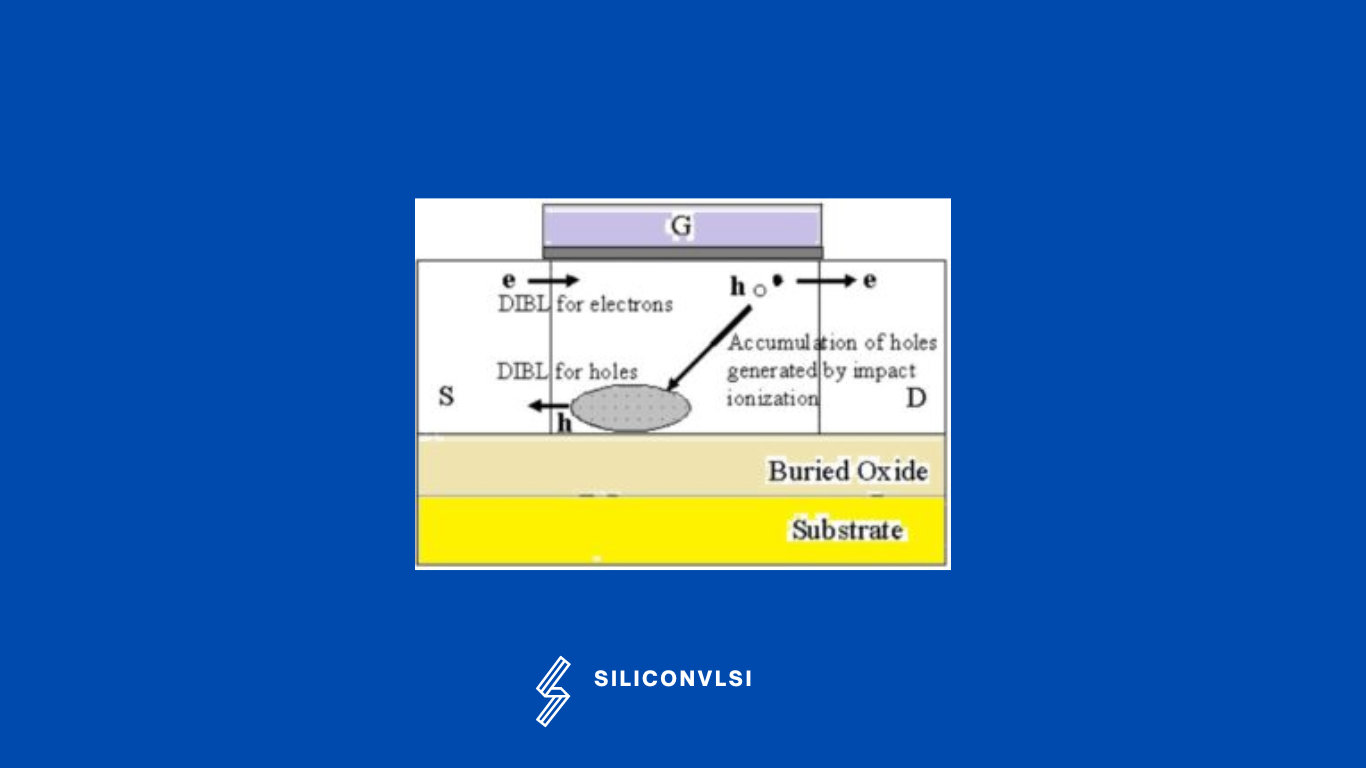
Holes generated near the drain due to impact ionization accumulate in the body region, and then positively bias the body, reducing Vt. This positive bias effect leads to Vt lowering for all gate lengths, including rather long gates such as 2 μm. The Hole generation rate due to impact ionization increases as gate length decreases under a fixed value of Vt.
The DIBL(Drain induced barrier lowering) effect on the barrier height for holes reduces the positive bias effect on the body because the accumulated holes in the body can more easily surmount the barrier and flow to the source. As a result, fewer accumulated holes remain which weakens the VT lowering. The potential near the bottom in the thin film increases as gate length decreases due to the drain electric field. This leads to the lowering of the barrier height for holes at the source edge near the bottom with shorter gate lengths.
![]()
Drain induced barrier lowering mechanism with shorter gate lengths, the barrier height for holes near the bottom is lowered by the influence of the drain electric field, and holes accumulated in the body region can more easily flow into the source