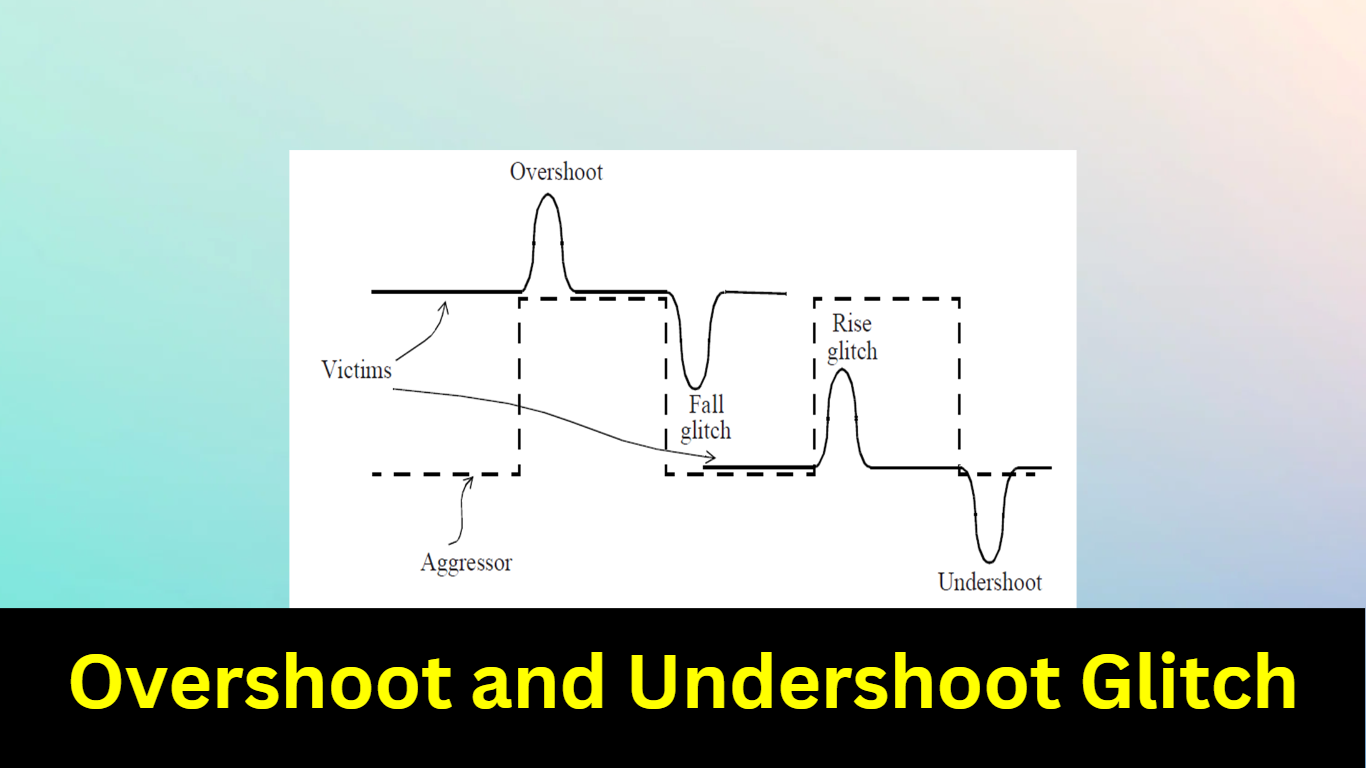
A glitch that takes the victim’s net voltage above its steady high value. Such a glitch is called an overshoot glitch. Similarly, a falling aggressor when coupled with a steady low victim net causes an undershoot glitch on the victim net.
Crosstalk Noise
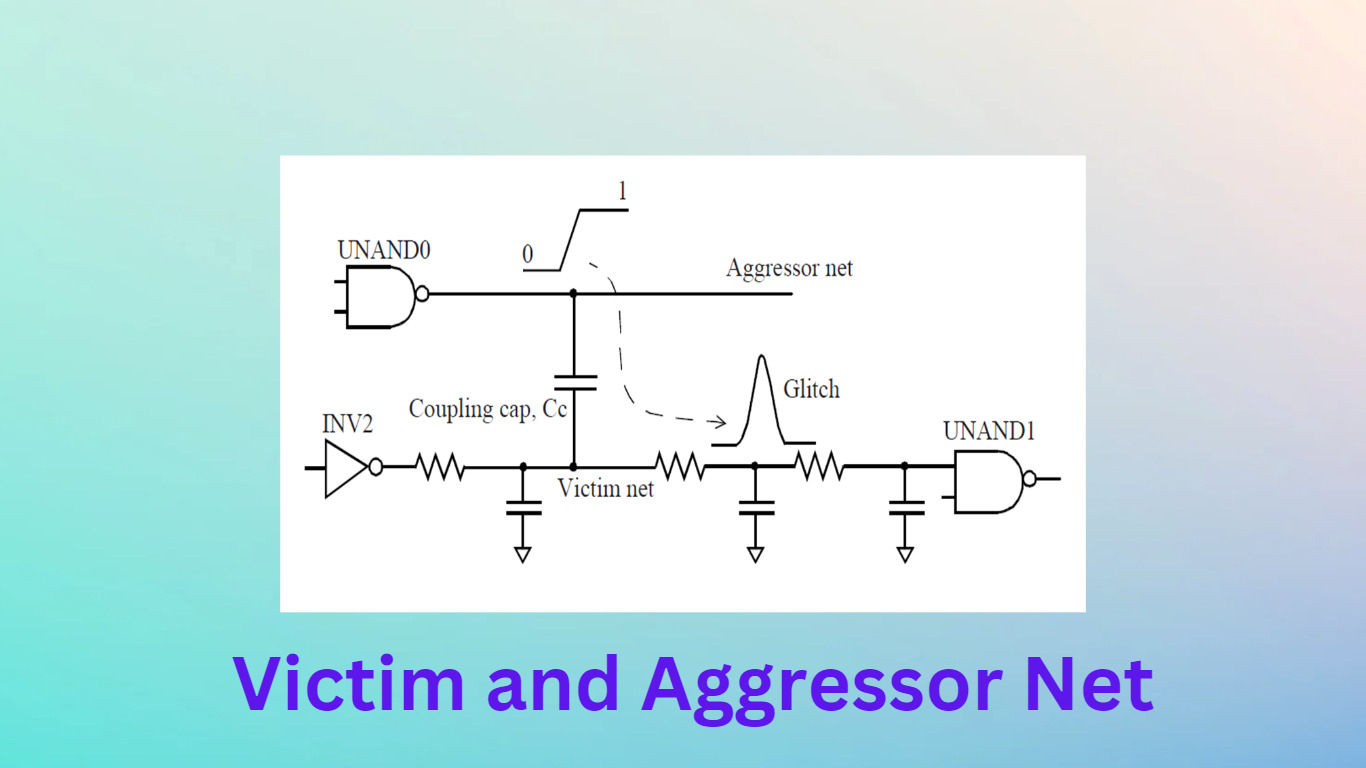
The crosstalk noise refers to unintentional coupling of activity between two or more signals. The crosstalk noise is caused by the capacitive coupling between neighboring signals on the die. This results in switching activity on a net to cause unintentional effects on the coupled signals. The affected signal is called the victim, and the affecting signals are termed as aggressors.
What is the Source of Noise in VLSI?
- Increase Metal thickness
- Lower supply voltage.
- Higher routing density due to Small geometry
- Vertically dominant metal aspect ratio.
- An increasing number of metal layers.
- A larger number of interacting devices and interconnects.
- Faster waveforms due to higher frequencies.
Two types of noise effects
Crosstalk Glitch: This refers to noise/glitch caused by a steady victim signal due to the coupling of switching activity of the neighboring aggressors.
Crosstalk Delay: This is due to the coupling between the switching activity of the victim and the switching activity of the aggressors, which results in the change of timing on a particular victim’s signals.
Types of Glitches
- Rise Glitches
- Fall Glitches
- Overshoot Glitches
- Undershoot Glitches
The magnitude of the glitch caused is dependent upon a variety of factors.
Some of these factors are:
- A slew of the aggressor net.
- Victim net driving strength.
- Victim net grounded capacitance.
- Coupling capacitance between the aggressor net and victim.
Crosstalk Delay Analysis
Crosstalk delay and crosstalk noise are essentially identical; the only distinction is that switching activity is occurring on both the victim and aggressor nets and that the nets are not at steady state values. The propagation orientation of the aggressor and victim nets affects crosstalk delay. As a result, victim nets transition either more slowly or more quickly.
Positive crosstalk delay
If the aggressor net is switching in the opposite direction of the victim net, it results in a larger delay for the victim net. The increase in delay is known as a positive crosstalk delay. This is shown below in Figure.
![]()
Negative crosstalk delay
If the aggressor and victim nets are switching in the same direction, it results in a smaller delay for the victim net. The reduction in delay is known as a negative crosstalk delay. This is shown below in Figure
![]()
