What is Dangling Bond?
A dangling bond occurs when an immobilized atom has an unsatisfied valence. Atoms typically strive to gain enough electrons to fill their valence shell, and they do this by forming covalent bonds with other atoms. In the simplest case, a single covalent bond forms when two atoms each contribute one unpaired electron, sharing these electrons between them.
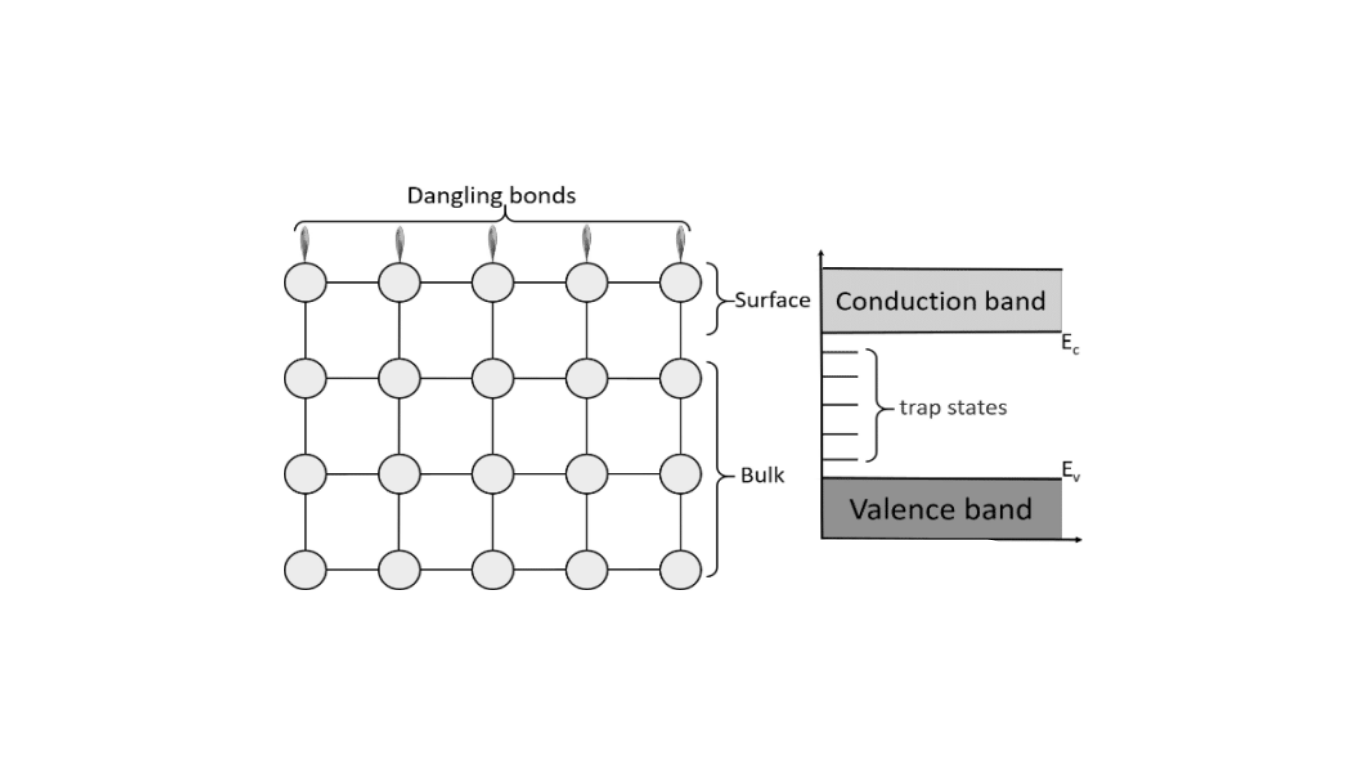
However, sometimes certain atoms don’t have enough bonding partners to satisfy their valences, leading to the presence of unpaired electrons. These atoms are called free radicals. Molecules containing such atoms are also termed free radicals. When a free radical exists in an immobilized environment, like a solid material, we refer to it as an “immobilized free radical” or a “dangling bond.”
Why Dangling Bonds Matter
When you with semiconductor devices—especially those involving semiconductor/electrolyte interfaces like in water-splitting photoelectrochemical cells—we often focus on how charge moves across the junction. Typically, we simplify this by using a Schottky barrier model. But in real-world devices, we quickly see that things aren’t that simple. We observe strong deviations in behavior, and a big reason behind that is the presence of dangling bonds on the surface of the semiconductor.
These dangling bonds create defect levels that can pin the Fermi level and shift the energy band edges, which directly affects the electrical performance of your device. Even when we try to passivate the silicon surface, a small number of these defects still remain, and surprisingly, they still dominate how well the device performs. Through our surface science studies—especially using techniques like photoelectron spectroscopy—we’ve seen firsthand how the electronic structure of differently prepared Si surfaces changes due to these surface states.
So, if you’re aiming for high-performance semiconductor devices, especially in applications like photoelectrochemical water splitting, you can’t afford to ignore dangling bonds. They might be tiny, but their impact on your device’s efficiency is huge. That’s why we believe detailed surface studies before and after electrochemical experiments are critical to truly understanding and improving device performance.
Also read: Understanding Voltage Drop in Electrical Circuits
In Summary
A dangling bond represents an unpaired electron on an immobilized atom. It occurs when an atom lacks enough bonding partners to complete its valence shell. These free radicals can be found in both atoms and molecules and are called “immobilized free radicals” when present in solid materials.