Diffusion current and Drift current
The diffusion and drift, both of which contribute to the conduction in semiconductors. Diffusion is characterized by the random motion of carriers occurring at all times and locations within the semiconductor. This process is akin to Brownian motion, where carriers move until they collide with lattice atoms, resulting in unpredictable angles of scattering. After a few collisions, the carriers’ motion becomes completely randomized. The diffusion of carriers can be likened to the diffusion of dye molecules in still water, where molecules gradually spread from regions of higher concentration to lower concentration, producing a diffusion current. Unless additional carriers are constantly introduced, diffusion eventually leads to the uniform redistribution of carriers throughout the semiconductor, and the diffusion current subsides.
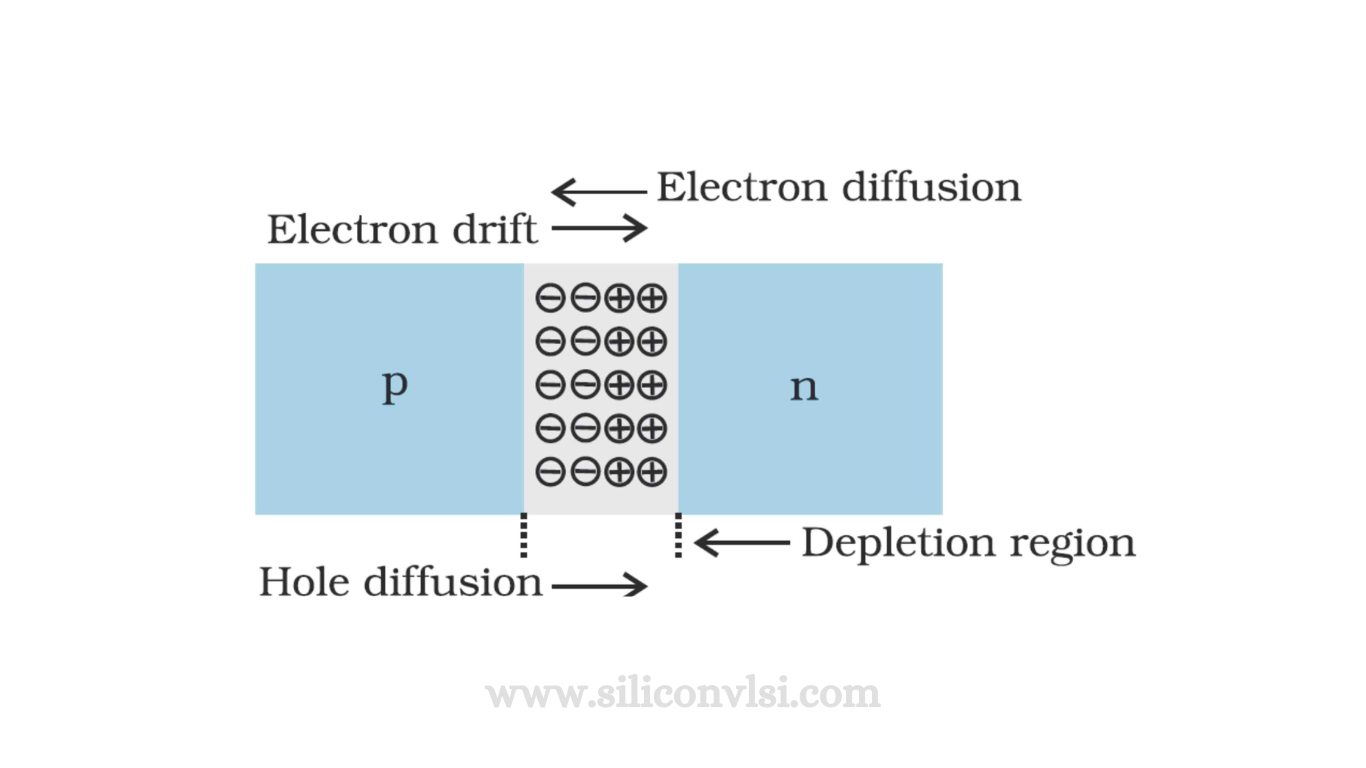
On the other hand, drift is the unidirectional movement of carriers influenced by an electric field. Despite the random drunkard’s walk caused by collisions with the lattice, carriers under the influence of an electric field gradually drift in a specific direction. The electric field consistently acts on the carrier, either retarding or accelerating its motion depending on the direction of movement. Frequent collisions prevent carriers from gaining significant velocity, but an overall subtle motion emerges. Electrons move toward positive potentials, and holes move toward negative potentials. A suitable analogy for drift is the motion of a steel ball in a pinball machine, where despite diverse directions caused by bumpers and pegs, the tilt of the board causes the ball to move downward. Similarly, an electric field biases carriers toward motion in a specific direction, resulting in a drift current.
In summary, the combined effects of diffusion and drift contribute to the motion of carriers in semiconductors. Diffusion leads to randomization and redistribution of carriers, producing a diffusion current, while drift, influenced by an electric field, imparts a subtle overall motion, generating a drift current. Both processes play integral roles in the conduction of semiconductors.
What is the difference between drift current and electric current?
Drift current is the electric current resulting from the movement of charge carriers influenced by an external electric field. On the other hand, diffusion current is the electric current caused by the diffusion of carriers, which leads to a change in carrier concentration.