POYNTING’S VECTOR
The transfer of energy between two conductors necessitates the presence of both a magnetic (H) and an electric (E) field. The H field corresponds to current flow, while the E field relates to the voltage across the lines. Throughout the space between conductors, the E-field direction is always perpendicular to the H-field direction, and both are perpendicular to the transmission path. The product of E X H at any point in space is known as Poynting’s vector, pointing in the direction of energy flow. E is measured in volts per meter, and H is measured in amperes per meter, resulting in watts per meter squared at a specific point in space.
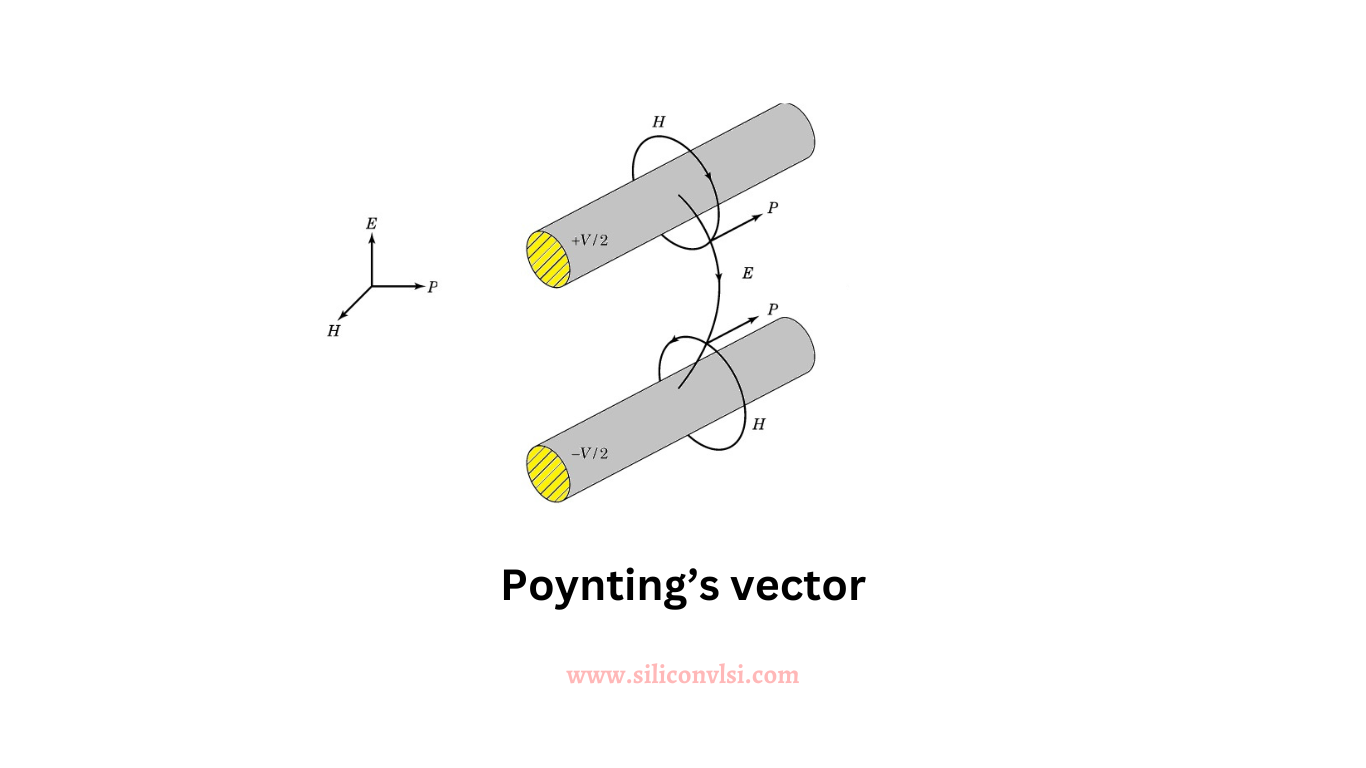
Consider a plane cutting perpendicular to the transmission line, as illustrated in Figure 1. Divide the plane into small regions with constant E and H values. Multiply these values by the area in each region and sum the results over the entire plane. The outcome is the power supplied by the battery, aligning with the circuit-based approach of volts multiplied by current.
What is the Right-Hand Rule?
Practically, the right-hand rule is employed by pointing the first two fingers and thumb at right angles to each other. The first two fingers represent the E- and H-field direction, respectively, while the thumb points in the direction of energy flow. If the E field is reversed, the hand must turn over, and the thumb points in the opposite direction, indicating the reversal of energy flow.