Channel Length in CMOS
In CMOS technology, the drain current—often referred to as the output current—of a transistor is affected by changes in the channel length. When we shorten the channel length, the drain current tends to increase. Conversely, if we lengthen the channel, the drain current decreases. This relationship is crucial for designing CMOS circuits because it allows us to control and enhance their performance. By tweaking the channel length, engineers can effectively regulate the drain current, which in turn influences how CMOS devices operate and function.
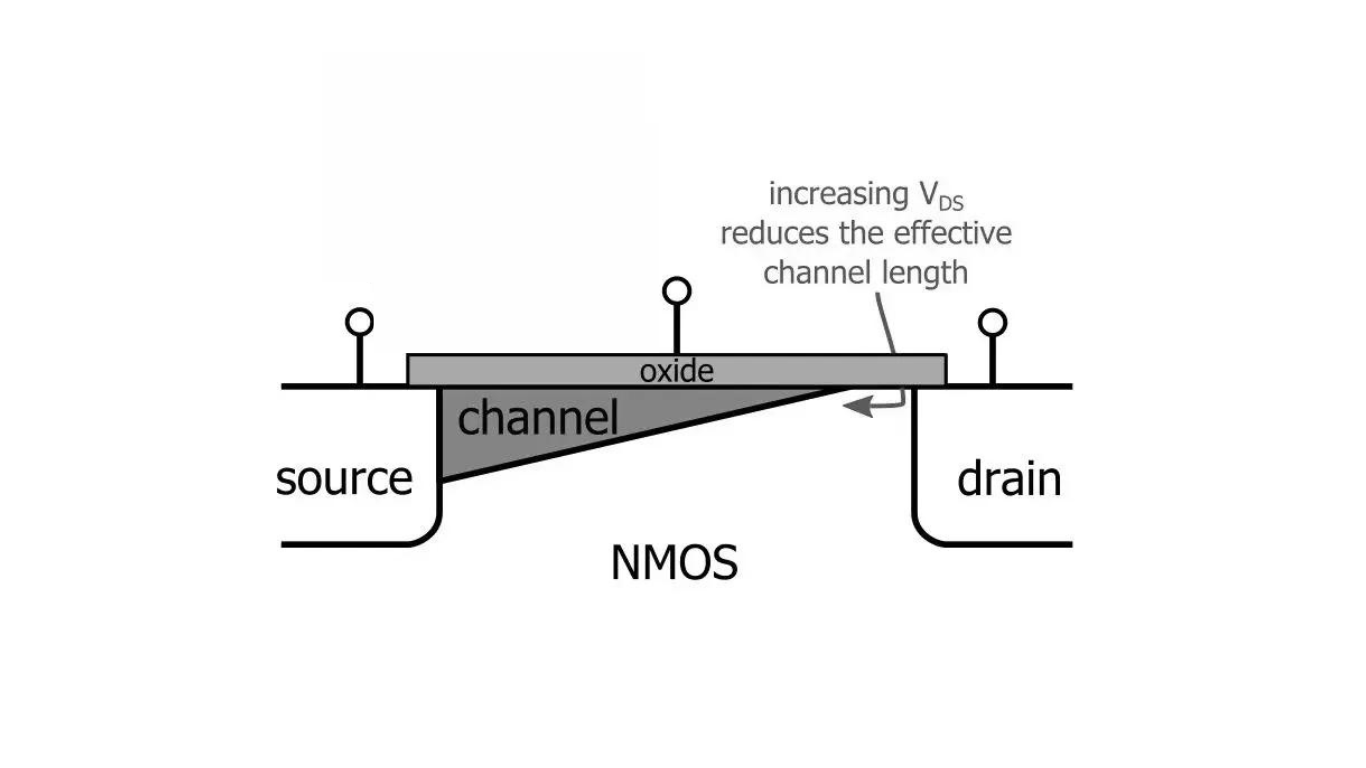
Channel length modulation is one of the short-channel effects we face during MOSFET scaling. When you or I increase the drain bias significantly, the inverted channel region becomes shorter. This leads to higher current with drain bias and causes the output resistance to decrease.
What is the difference between a long channel and a short channel?
there are two types of devices with different channel lengths: short channel length and longer channel length. Short channel-length devices offer better performance and speed compared to longer channel-length devices. However, the longer channel length devices have a significant advantage in reducing subthreshold leakage current. The table below summarizes the comparison of speed versus channel length for these devices.
What is the drain voltage?
In simple terms, drain-source voltage is the highest voltage allowed across the drain and source terminals of a power transistor when it is turned off. If this voltage goes beyond the limit, the power transistor enters a breakdown region and may not work properly.
What is the drain current controlled by?
The flow of current between the drain and the source of a transistor can be controlled by changing the voltage applied to the gate and source. This control is based on the principle of a depletion region, which is why it is sometimes called a depletion-mode device.