What is Threshold Voltage? A Key Parameter in MOSFET Operation Explained
The threshold voltage, also known as the “threshold” or “Vth”, is a critical parameter in the operation of a metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistor. It is the voltage that must be applied to the gate of the MOS transistor to turn it on and allow a significant current to flow between the source and drain.
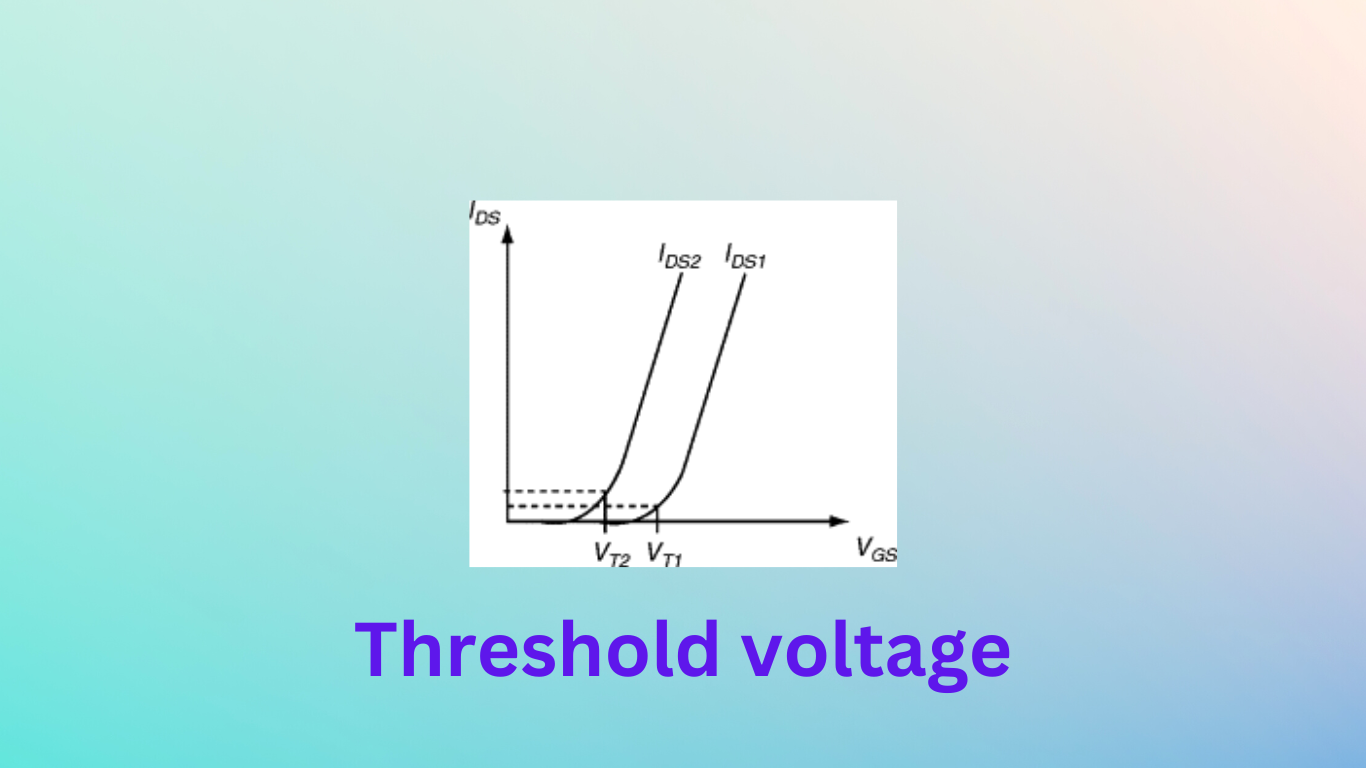
Threshold voltage in CMOS
The MOS transistor’s switching properties, including its on-state resistance, transconductance, and turn-on delay time, are determined by the threshold voltage. The amount of doping in the source and drain regions, the thickness of the oxide layer, and the kind of gate material all have an impact on the threshold voltage.
The threshold voltage is a key factor in defining the point in digital circuits where the MOS transistor flips from the off state to the on state. In order to guarantee that the MOS transistor can function dependably under a variety of process, voltage, and temperature fluctuations, this threshold point is frequently established at a specified voltage value.
What is threshold voltage in diode?
Diodes require a minimum threshold voltage, or Vth, between the anode and cathode in order for current to flow. This voltage is typically approximately 0.7V. No current will pass through the diode if the anode voltage is not at least Vth larger than the cathode voltage.#
Why does threshold voltage increase?
When a back bias is applied, the threshold voltage rises. A larger depletion region is produced by a positive bias on the substrate, which also helps keep the gate charge in check. As a result, there are fewer electrons present in the inversion layer.#
Does threshold voltage change with temperature?
As temperature rises, the threshold voltage decreases, and the subthreshold leakage current increases exponentially with an increase in temperature.#
Is the threshold voltage and knee voltage the same?
A significant forward current must start flowing across the diode before a potential difference equal to the barrier potential is reached at room temperature. This value is often referred to as the “(V th)” threshold voltage, “cut-in voltage,” or “knee voltage.”