Understanding Amplitude Modulation
The amplitude modulation(AM) technique is used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. Amplitude modulation is a form of modulation used for radio transmissions for broadcasting and two-way radio communication applications.
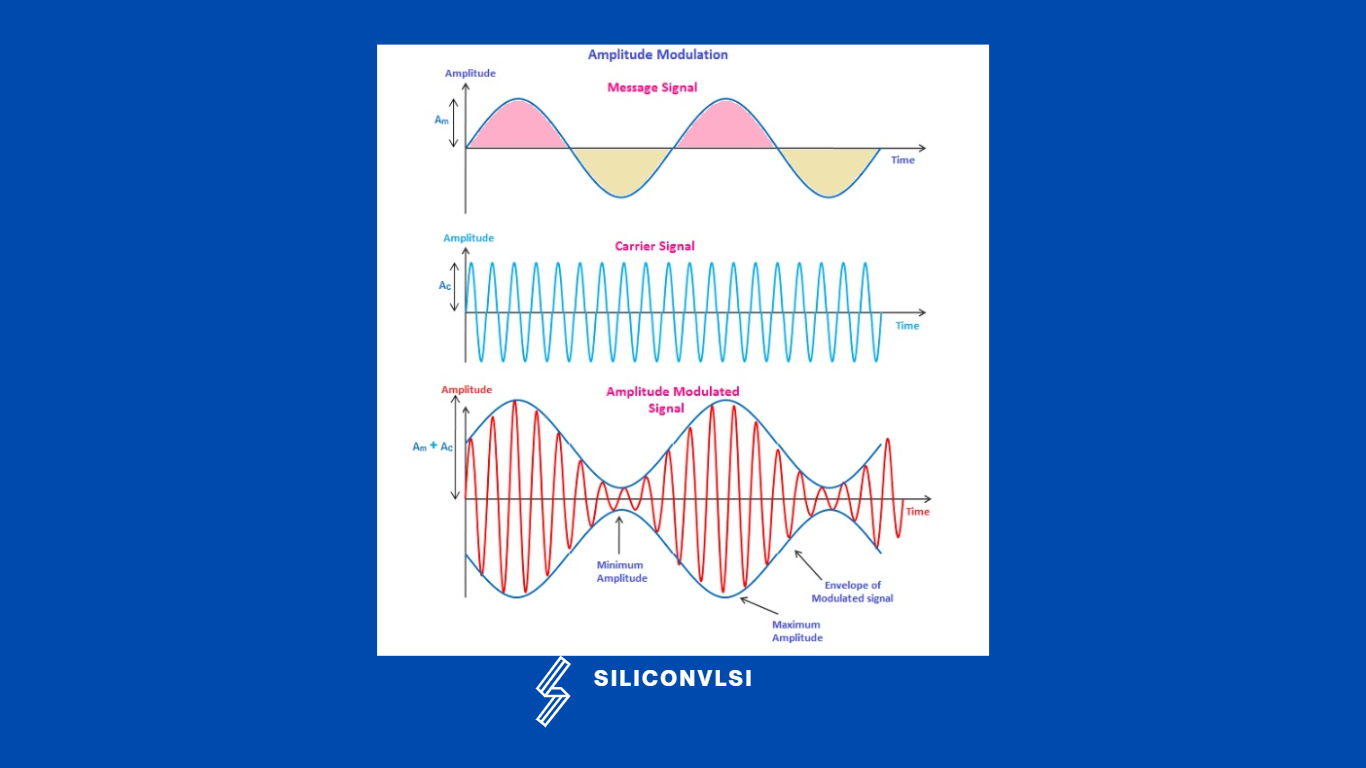
Amplitude modulation is a type of modulation where the height of the carrier signal is changed in accordance with the height of the message signal. One of the key reasons for the use of amplitude modulation was its ease of use. The system simply required the carrier amplitude to be modulated, but more usefully the detector required in the receiver could be a simple diode-based circuit.
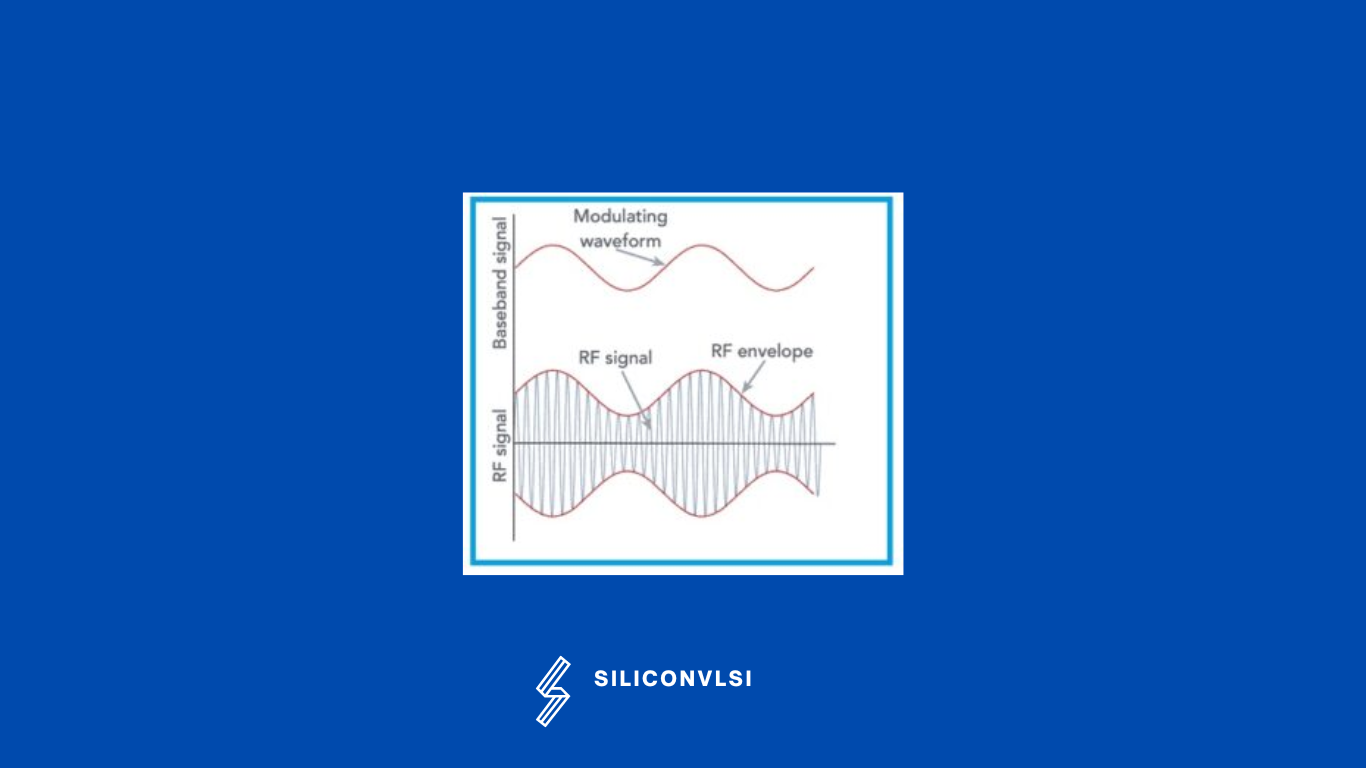
In order that a radio signal can carry audio or other information for broadcasting or for two-way radio communication, it must be modulated or changed in some way. Although there are a number of ways in which a radio signal may be modulated, one of the easiest is to change its amplitude in line with variations of the sound. In this way, the amplitude of the radio frequency signal varies in line with the instantaneous value of the intensity of the modulation.
Types of Amplitude Modulation
There are three main types of amplitude modulation
Double Sideband-suppressed Carrier Modulation (DSB-SC)
Single Sideband Modulation (SSB)
Vestigial Sideband Modulation (VSB)
Mathematical Expression
Consider a sinusoidal modulating signal or message signal (am) of frequency (ωm) and amplitude (Am) given by:
am = Am sin ωmt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (1)
and carrier wave (ac) of frequency (ωc) and amplitude (Ac) given by:
ac = Ac sin ωct . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (2)
Where,
- am is the modulating signal or message signal
- ac is the carrier signal
- Am is the maximum amplitude of the message signal
- Ac is the maximum amplitude of the carrier signal
- ωm is the frequency of the message signal
- ωc is the frequency of the carrier signal
Using the above mathematical expressions, we can create a new mathematical expression for the complete modulated wave.
The amplitude-modulated wave (A) is given as:
A = ac + am. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (3)
Put am value from equation (1) into equation (3), then we get
A = ac + am sin ωmt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (4)
The instantaneous value of the amplitude-modulated wave (a) can be given as:
a = A sin θ
a = A sin ωct . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (5)
Put A value from equation (4) into equation (5), then we get
a = (Ac + Am sin ωmt) sin ωct . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (6)
This is an equation of amplitude modulated (AM) wave.
Advantages of Amplitude Modulation
- Low cost
- Few components needed
- It is simple to implement
- Long-distance communication
- it can be demodulated using a circuit consisting of very few components
Disadvantages of Amplitude Modulation
- It requires high bandwidth
- Amplitude modulation is prone to high levels of noise
- It is inefficient in terms of its power usage
- Amplitude modulation cannot be used for the transmission of sensitive information
- It is a type of transmission that can be easily affected by external radiation.
- Amplitude modulation (AM) cannot be used for transmitting music Frequency modulation (FM).
Use of Amplitude modulation | Amplitude modulation applications
- Airband radio
- Single sideband
- Broadcast transmissions
- Quadrature amplitude modulation