Intrinsic semiconductor: Fundamentals of Semiconductor physics
Intrinsic Semiconductor comes in between conductor and insulators. It is e made from the purest form of semiconductor material. The best examples of Intrinsic Semiconductor are Silicon & Germanium
| Silicon | 1s2 2s22p6 3s2 3p2 |
| Germanium | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2 |
- An intrinsic semiconductor, such as pure silicon has an equal number of electrons and holes.
- In a P-type semiconductor, holes are the majority charge carriers electrons called minority carriers.
- In N-type semiconductors, electrons are the majority charge carriers and holes are the minority carriers
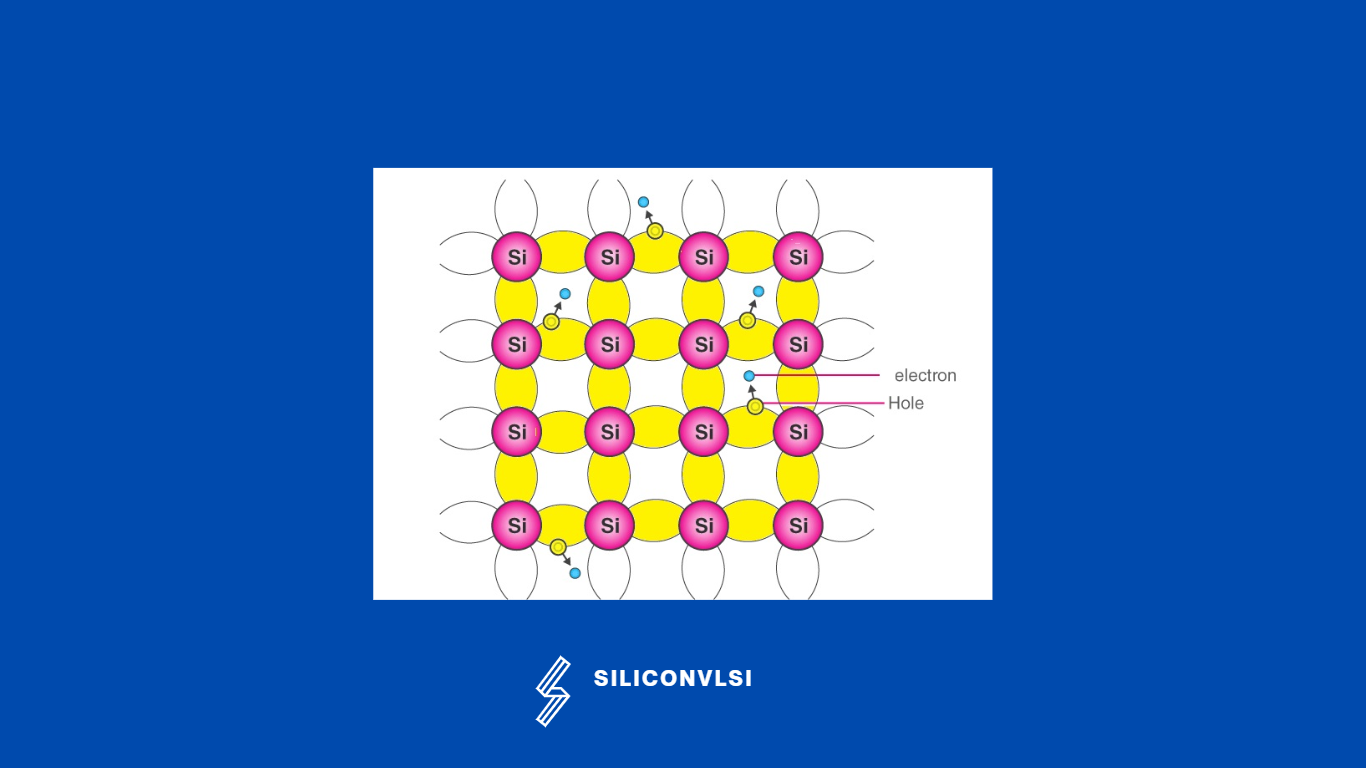
Use of Intrinsic Semiconductor
An intrinsic semiconductor is also called an undoped semiconductor. Silicon and germanium are the most common examples of intrinsic semiconductors. Both these semiconductors are most frequently used in the manufacturing of transistors, diodes, and other electronic components.
What is Electron current and Hole current?
Electron current: The current which flows in a circuit due to the flow of electrons, is the electron current. The direction of the electron is negative to positive.
Hole current: The current which flows in a circuit due to the flow of holes, is the hole current. The direction of the hole is positive to negative.
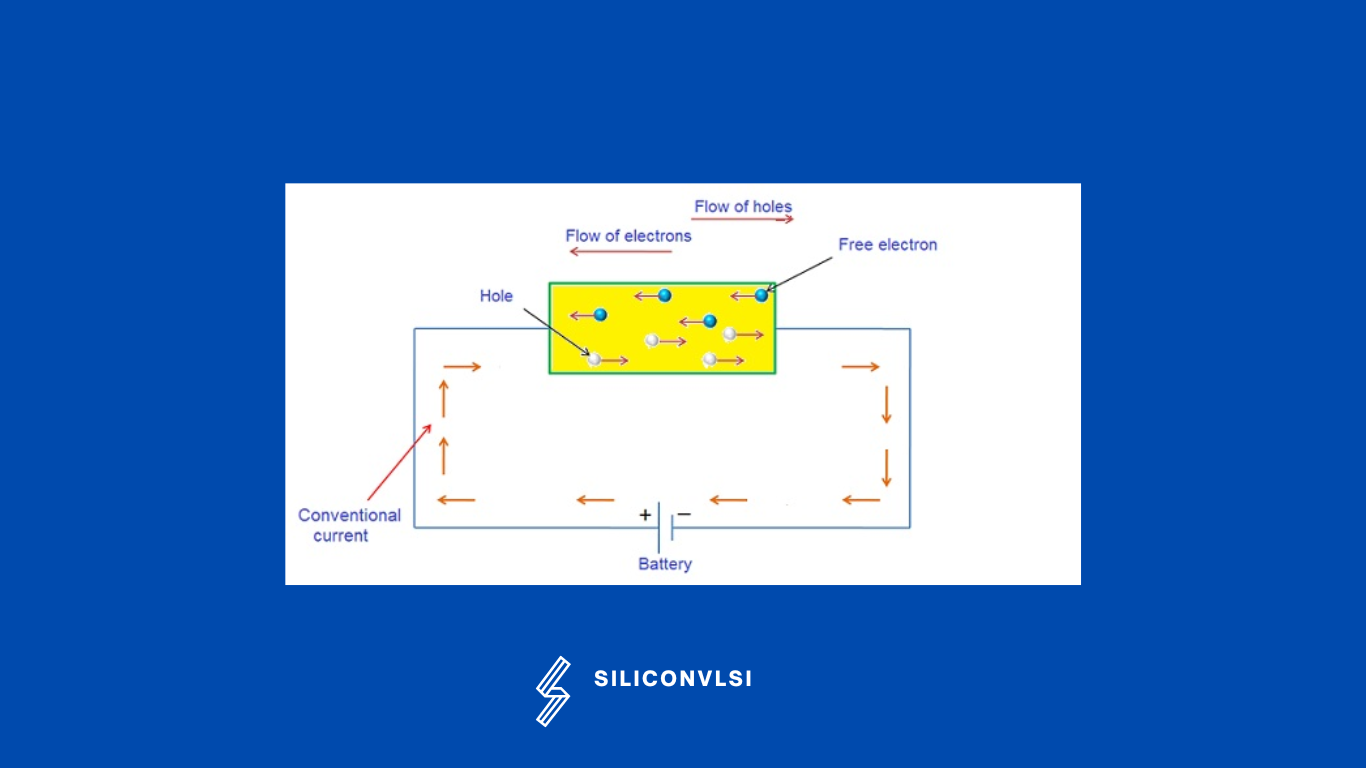
In other words, we can say that a Current that is caused by electron motion is called electron current, and a current that is caused by hole motion is called hole current. An electron is a negative charge carrier whereas a hole is a positive charge carrier.
- N Type Semiconductor
- P Type Semiconductor
- Intrinsic Semiconductor
- Extrinsic Semiconductor
- Difference Between Donor and Acceptor Impurities
- Difference Between p-Type and n-Type Semiconductor
- Electron Hole Pairs Generation and Recombination