What is EPI in Silicon VLSI Technology?
EPI stands for Epitaxial Silicon layer. The EPI layer is doped appropriately for the best transistor performance which means more lightly doped than the remaining lower portion of the substrate that is highly doped.
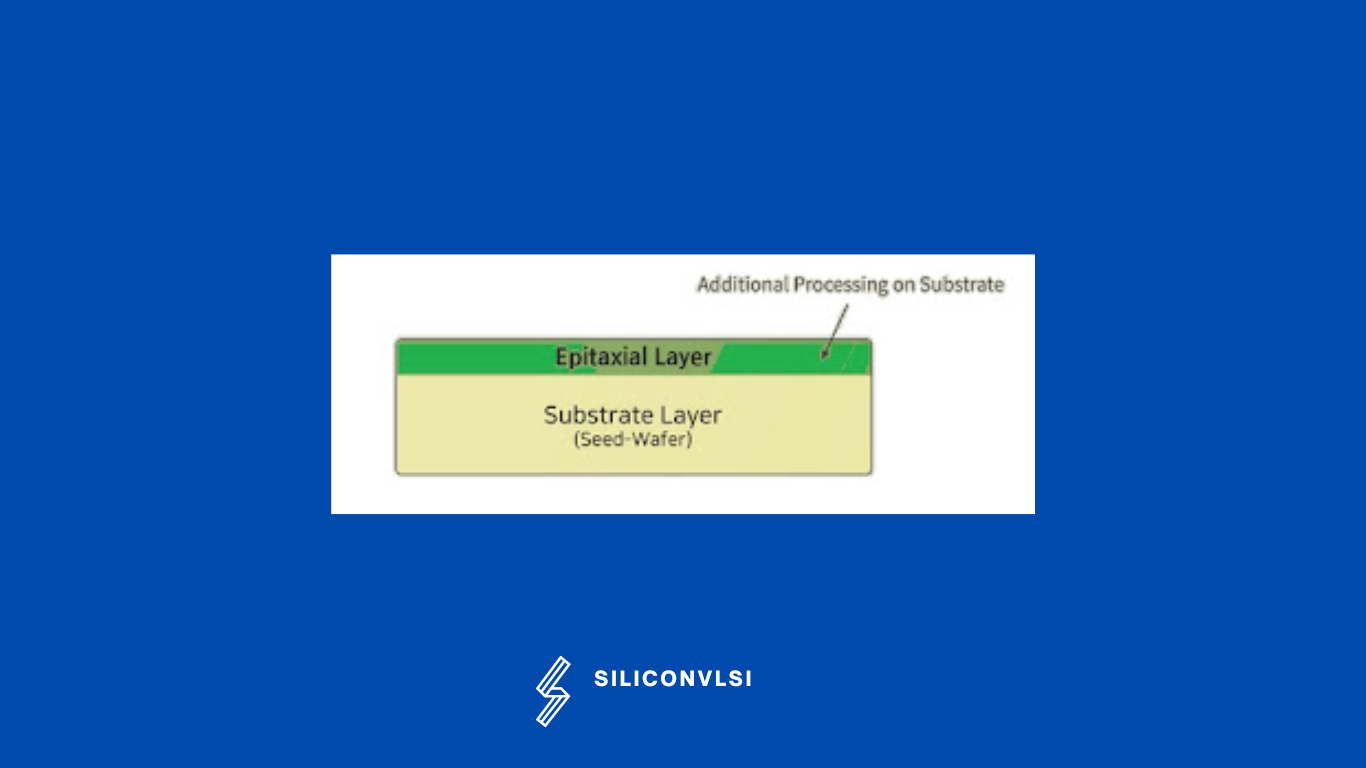
The highly doped substrate directs majority carriers to the ground and reflects minority carriers making the guard rings more effective.
This Epitaxial Silicon layer helps to avoid the Latch-up problem in CMOS VLSI technology.
Epitaxial Silicon Wafer for IC and Power Applications
Silicon epitaxy is a complex process where an additional layer of monocrystalline silicon is deposited onto the polished surface of a silicon wafer. Unlike simple epitaxy, silicon epitaxy involves multiple simultaneous chemical reactions. During epitaxial layer growth, chemical substances are deposited on top of an existing crystal layer, resulting in layered growth, also known as “stacking.” Silicon-based devices can be fabricated using this process, with layers formed in two different directions.