What is a Zener diode?
A zener diode is a heavily doped semiconductor device that is designed to operate in the reverse direction.
or
If the reverse-biased voltage applied to the p-n junction diode is highly increased, a sudden rise in current occurs. At this point, a small increase in voltage will rapidly increase the electric current. This sudden rise in electric current causes a junction breakdown called Zener or avalanche breakdown.
Symbol of Zener diode
The symbol of the Zener diode is similar to the normal p-n junction diode but with bent edges on the vertical bar. Zener diode consists of two terminals: cathode and anode. its electric current flows from both anode to cathode and cathode to anode.
How does a Zener Diode work in reverse bias?
A Zener diode operates just like a normal diode when it is forward-biased. When connected in reverse-biased mode, a small leakage current flows through the diode. As the reverse voltage increases to the predetermined breakdown voltage (Vz), the current starts flowing through the diode. The current increases to a maximum, which is determined by the series resistor, after which it stabilizes and remains constant over a wide range of applied voltage.
The Zener diode is more heavily doped than the normal p-n junction diode. Hence, it has a very thin depletion region. Therefore, Zener diodes allow more electric current than normal p-n junction diodes. A Zener diode allows electric current in a forwarding direction like a normal diode but also allows electric current in the reverse direction if the applied reverse voltage is greater than the Zener voltage. Zener diode is always connected in the reverse direction because it is specifically designed to work in a reverse direction.
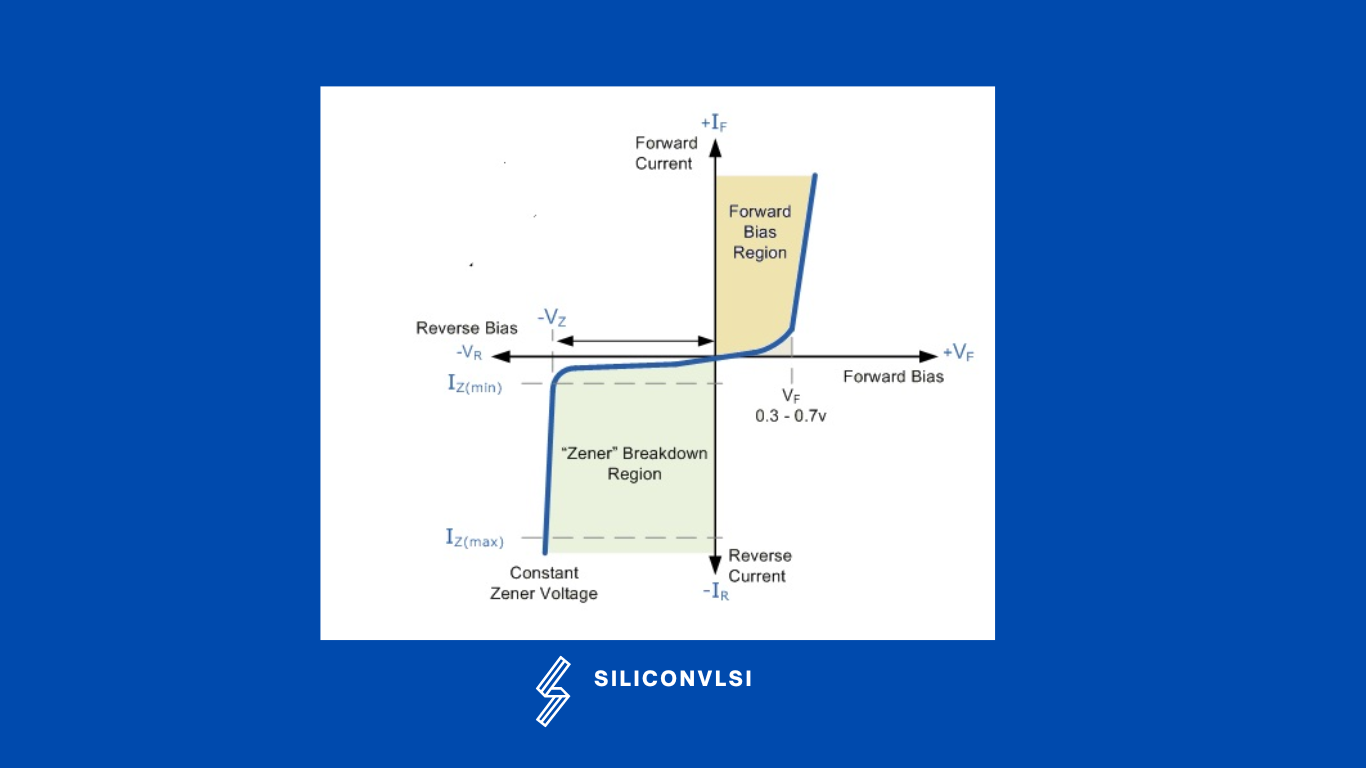
VI characteristics of Zener diode
The VI characteristics of a Zener diode are shown in the below figure. When forward-biased voltage is applied to the Zener diode, it works like a normal diode. When reverse-biased voltage is applied to a Zener diode, it allows only a small amount of leakage current until the voltage is less than the Zener voltage. Once voltage applied to the Zener diode reaches Zener voltage, it starts allowing a large amount of electric current. At this point, a small increase in reverse voltage will rapidly increase the electric current. This is the main advantage of the Zener diode. Because of this sudden rise in electric current, a breakdown occurs called Zener breakdown. However, the Zener diode exhibits a controlled breakdown that does damage the device.
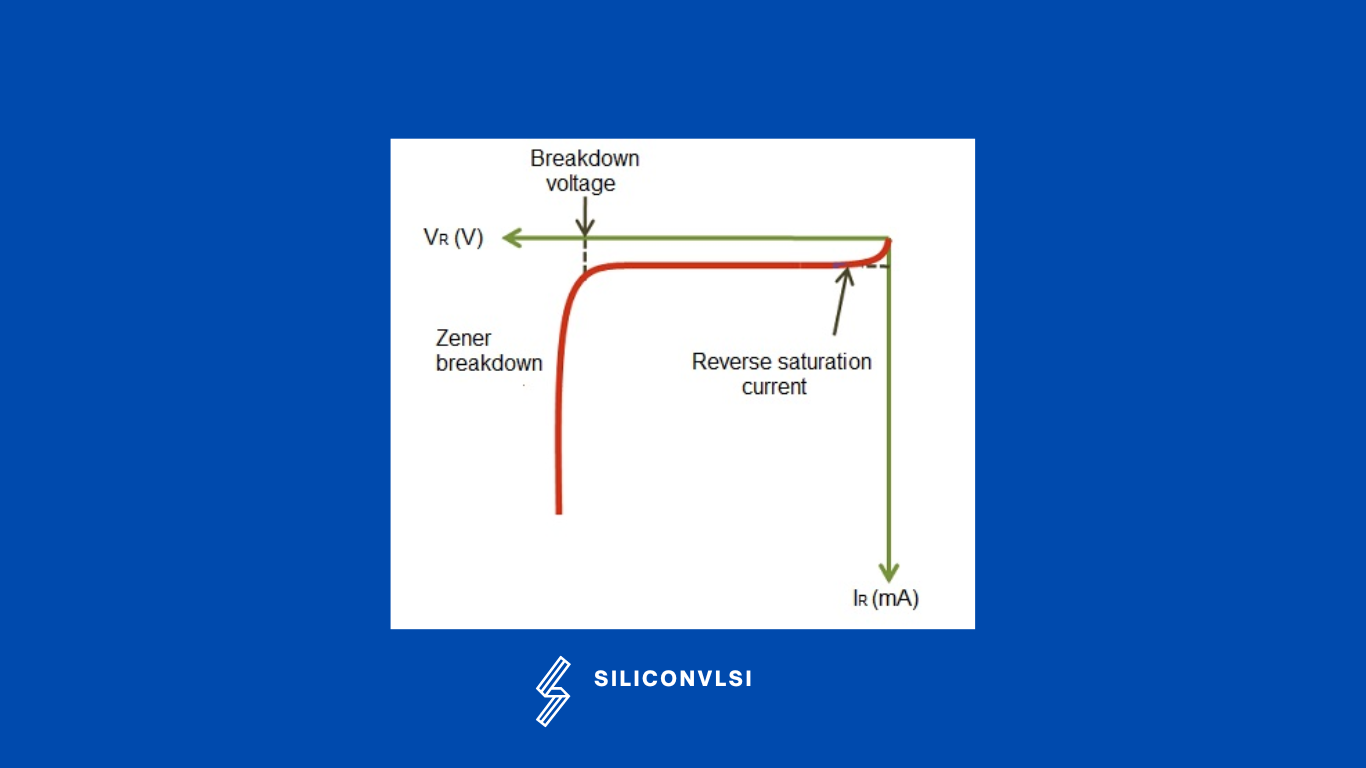
The Zener breakdown voltage of the Zener diode depends on the amount of doping applied. If the diode is heavily doped, Zener breakdown occurs at low reverse voltages. If the diode is lightly doped, the Zener breakdown occurs at high reverse voltages. Zener diodes are available with Zener voltages in the range of 1.8V to 400V.
Advantages of Zener diode
- Low cost
- Small size
- High accuracy
- Power dissipation capacity is very high
Applications of Zener diode
Zener diode used as
- Voltage reference
- Witching operations
- Various protection circuits
- Clipping and clamping circuits.
- Voltage stabilizers or shunt regulators.
- Clipping and clamping circuits.
Difference Between the Zener diode and Avalanche diode
The difference is that the Zener effect is a quantum phenomenon and the avalanche effect is the movement of electrons in the valence band like in an electric current. The Zener effect is dominant in voltages up to 5.6 volts and the avalanche effect takes over above that. The Avalanche effect also allows a larger current through the diode than what a Zener breakdown would allow.
Zener Diode Specifications
- Voltage Tolerance – It is typically ±5%
- Temperature Stability – Diodes around 5 V have the best stability
- Zener Resistance (Rz) – It is the resistance to the Zener diode exhibits.
- Power Rating – It denotes the maximum power the Zener diode can dissipate.
- Zener Voltage – The Zener or the reverse breakdown voltage ranges from 2.4 V to 200 V
Types of Diodes
- Zener diode
- Avalanche diode
- Light Emitting Diode
- Laser diode
- Tunnel diode
- Schottky diode
- Varactor diode
- P-N junction diode