What is a MOSFET in VLSI: Working and Its Applications
The MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) is a semiconductor device that is widely used for switching purposes and for the amplification of electronic signals in electronic devices. A MOSFET is a four-terminal device having source(S), gate (G), drain (D), and body (B) terminals. The body of the MOSFET is connected to the source terminal, resulting in a three-terminal device similar to a field-effect transistor. MOSFET is generally considered a transistor and is employed in both analog or digital circuits. This is a basic overview of MOSFETs. The general structure of this device is as below
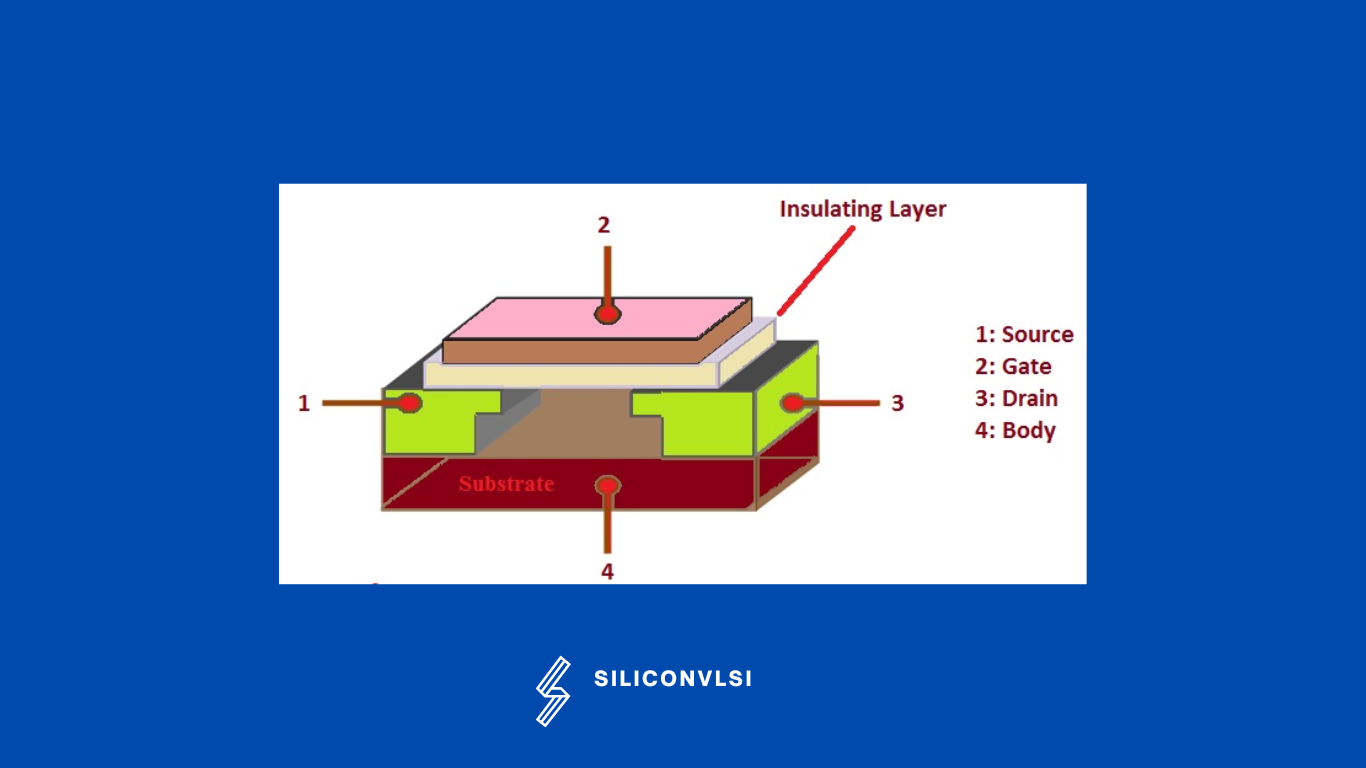
The functionality of MOSFET
- Enhancement Mode
- Depletion Mode
Enhancement-type MOSFETS
When the gate voltage is negative with respect to the source, MOSFET operates with an enhancement mode known as enhancement type MOSFET. Enhancement-type MOSFETS are normally off. When you connect an enhancement-type MOSFET, no current flows from the drain to the source, when there is no voltage applied to its gate. This is why it is called a normally-off device. There is no current flow without a gate voltage.
Depletion-type MOSFETS
When the gate voltage is positive with respect to the source, the MOSFET operates in depletion mode is known as depletion-type MOSFET. Depletion MOSFETs are normally on devices. They conduct current at the maximum level when there is no voltage applied to the gate. In depletion-type MOSFET, as you increase the gate-source voltage, the drain-source channel of the transistor becomes more resistive and the current flowing from drain to source decreases, The current stops flowing completely when the gate-source voltage reaches the cutoff level.
Application of MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET)
MOSFETs are used in electronic devices to switch and amplify electronic signals.
- It can be used as a resistor, capacitor, or inductor.
- It functions as an inverter.
- It is suitable for usage in digital circuits.
- A high-frequency amplifier can be made with a MOSFET.
- It can be used to power brushless DC motors and DC relays.
MOSFET Regions of Operation
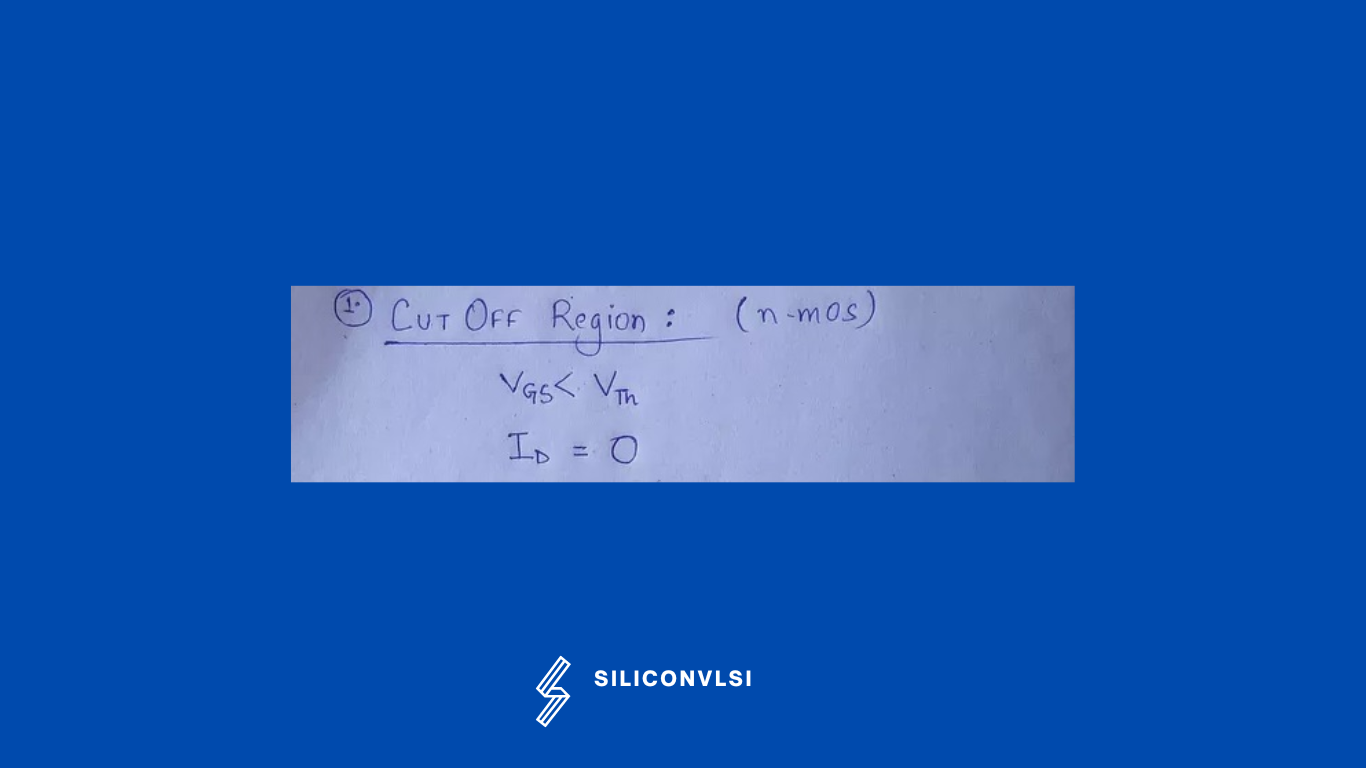
Cut-off Region
This is the region where the device is turned off and there is no current flowing through it. The device serves as a basic switch in this instance, and it is used when electrical switches are required.
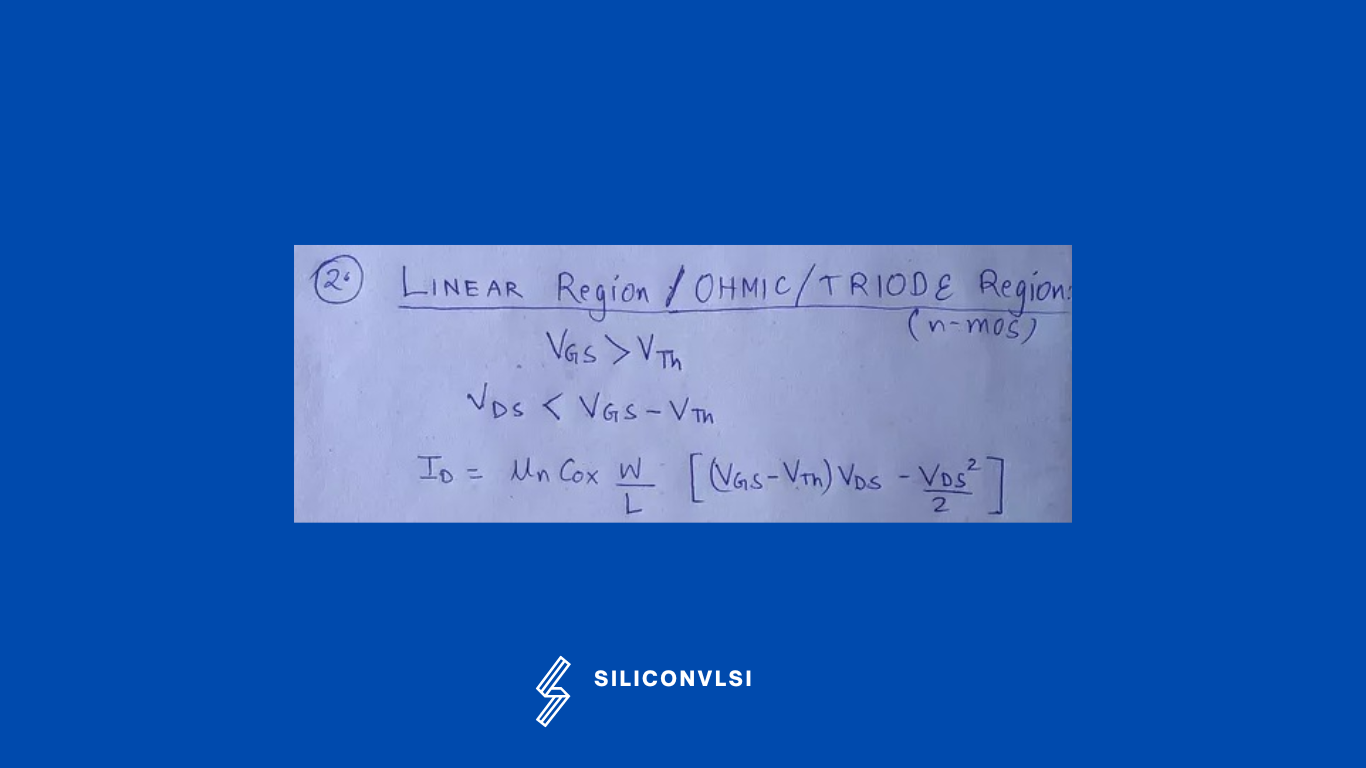
Linear Region
It is also called an ohmic region, in which the current across the drain to the source terminal enhances with the increment in the voltage across the drain to the source path. When the MOSFET devices function in this linear region, they perform as an amplifier functionality.
Saturation Region
In this region, the devices’ drain-to-source current values will remain constant despite the increased voltage across the drain to the source. When the voltage from the drain to the source terminal exceeds the pinch-off voltage value, this happens only once. In this case, the device acts as a closed switch, with a saturated current flowing from the drain to the source terminals. As a result, when the devices are supposed to switch, the saturation region is chosen.

Is MOSFET an active device?
Yes, we call them “active” because they can change their state dynamically depending on a control signal rather than stay on the same status all the time no matter how conditions change
Why is MOSFET a voltage-controlled device?
The gate of a MOSFET is isolated by an insulator, which means no current can flow. The presence of a voltage at the gate creates an electric field in the semiconductor channel that makes it conductive. That’s why it is called a voltage-controlled device