Difference between Schematic and Layout.
A Schematic is a “Circuit Diagram” or a drawing of how it will work. A “Layout” is the circuit board or Physical representation of the schematic.
What is Schematic Diagram?
The schematic is a drawing that defines the logical connections between components on a circuit board whether it is a rigid PCB or a flex board. A schematic diagram is a visual representation of a process, device, or other object’s parts using standardized, frequently abstract symbols and lines. Although schematic diagrams are frequently related to electrical circuits, there are numerous instances in other fields as well.
Rules for drawing schematic diagram
- Wires must not cross and connect.
- Label pin numbers on the outside of a symbol, and signal names on the inside.
- Any critical or Matching device information should be mentioned in text format.
- Wires and components are aligned horizontally or vertically unless there’s a good reason to do otherwise.
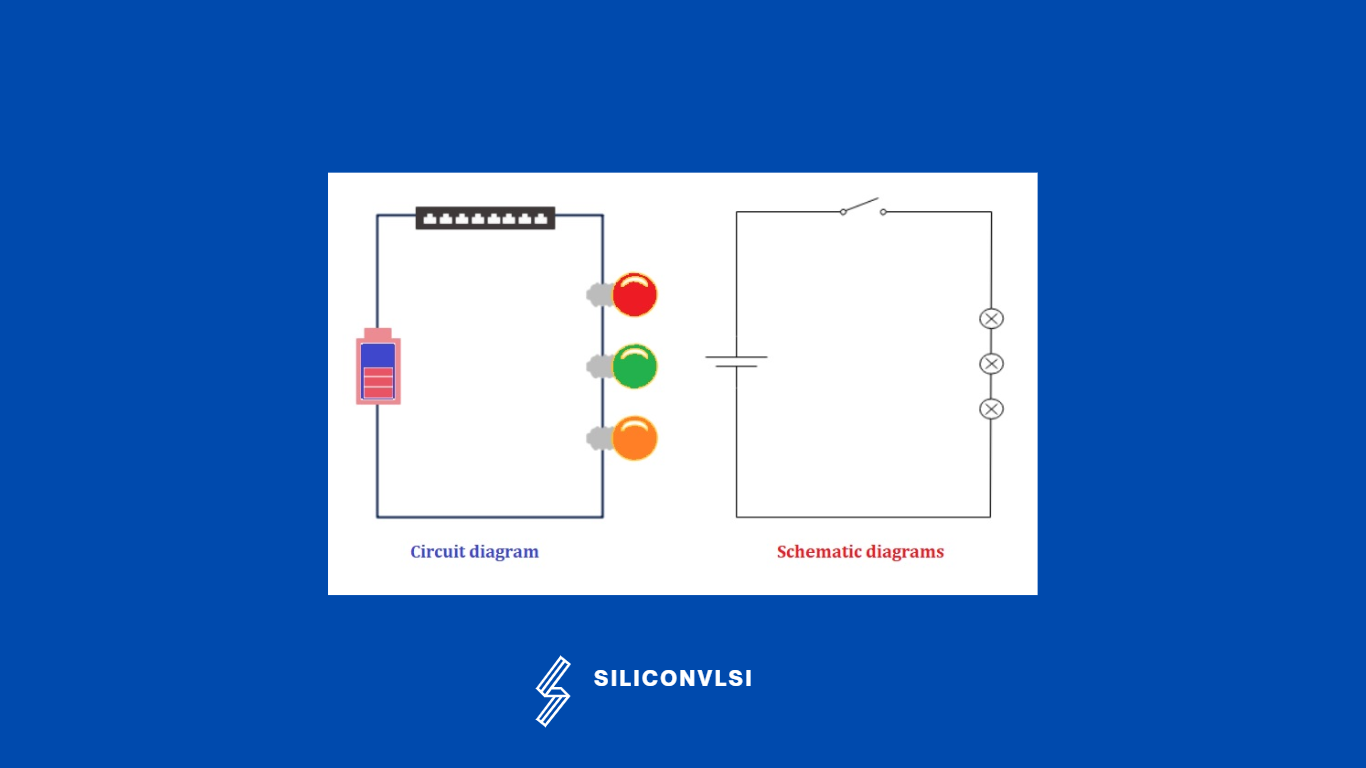
Differences between Schematic Diagrams and Circuit Diagrams
Engineering diagrams frequently make use of schematics and circuit diagrams. Even though you’ve probably heard them a lot, they do differ differently from one another. Their intended audiences or readers are different; whereas skilled schematic viewers frequently use schematics, beginners can easily understand circuit diagrams.
You will have a thorough understanding of the usefulness of diagrams in identifying the parts of an electric system, tracing a circuit, or even fixing electrical equipment after seeing an illustration of the distinctions between schematic diagrams and circuit diagrams.
What is Layout?
A larger integrated circuit is created using a VLSI layout, which incorporates many smaller circuits. Building essential circuit blocks and incorporating them into a bigger system are the first steps in this design technique. A series of circuit simulations are utilized to optimize each circuit block when creating circuit blocks prior to the VLSI layout.
Layout design rules VLSI
On MOSIS rules, design regulations are based. Parameter lambda is the most important phrase in MOSIS rules. There are several levels of design rules.
- Well, rules
- Transistor rules
- Contact rules
- Metal rules
- Via rules
Well Rules
- N-well transistor implants are put more deeply than any other type. The distance between the margins of n-wells and the diffusion of n+ should be sufficient. Typically, the oxide transition time across the good barrier determines this clearance. The second guideline calls for grounding n-well and ensuring an adequate number of good taps. Due to the well current, this will stop severe voltage dips.
Transistor rules
- Polysilicon mask – crossing of polysilicon and diffusion mask defines the gates of the transistor.
- Active mask – defines where p- or n-diffusion type or gates will be placed.
- n-implant mask – defines areas where n-type diffusion is required.
- p-implant mask – defines where p-type diffusion is required.
Contacts rules
- metal to p-active
- metal to n-active
- metal to polysilicon
- metal to well or substrate
Metal rules
- Depending on the metal line, the metal spacing rule may vary. However, both thin and thick wires must adhere to a particular width. Therefore, if wider cables are required, they can be created by connecting numerous small wires. Long parallel wires can be arranged according to spacing regulations.
![]()