What Is Double Patterning in VLSI?
Double patterning is a widely used technique in advanced semiconductor manufacturing processes, especially at smaller process nodes. This technique involves using lithography methods to define the features of integrated circuits more precisely. By employing double patterning, designers can fabricate chips at sub-nanometer process nodes, ensuring high performance and functionality. The double patterning process typically involves litho-etch-litho-etch (LELE) pitch-splitting steps within the fabrication facility. Another approach known as self-aligned double patterning (SADP) utilizes spacer methods as part of the double patterning process, enabling even greater precision in feature definition.
The fabrication of MOSFETs is done using light of wavelength 193nm in a process called Optical lithography. Now as we move towards lower technology nodes i.e. channel length below 30nm, the process can lose its accuracy. The quality is lost due to the diffraction of light around the corners and edges of the mask since the features are too small compared to the wavelength of light. This results in uneven edges, shorts, or the complete absence of the metal to be etched. This is where double patterning comes into the picture.
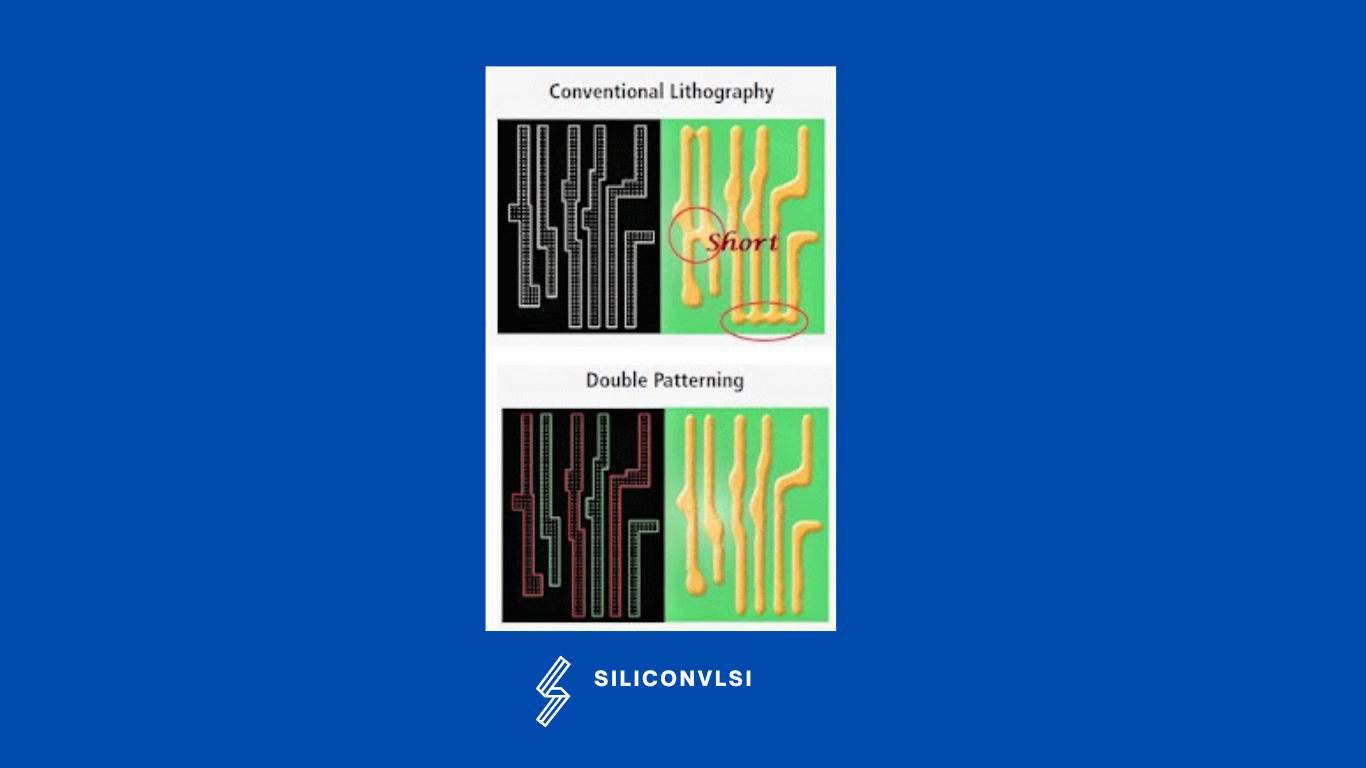
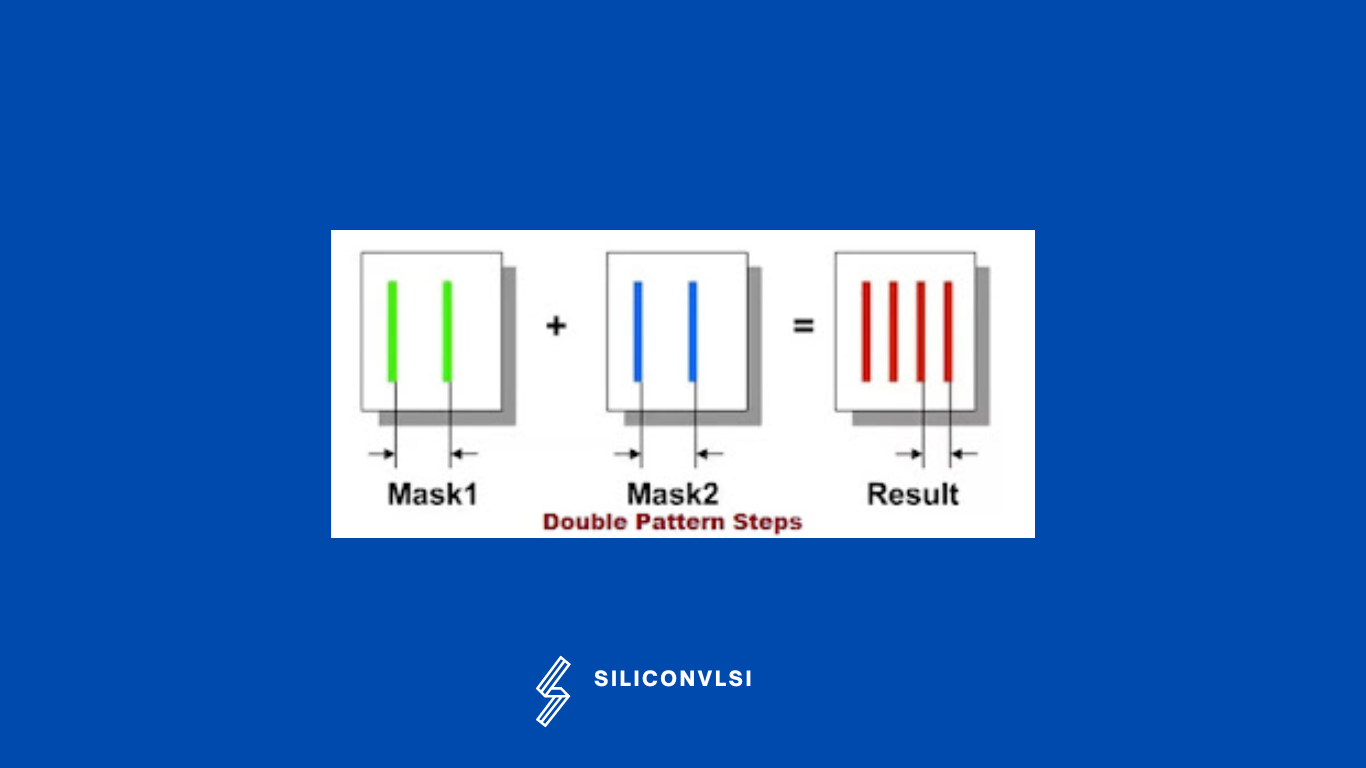
In this method, dense patterns of metals in a single mask are split into 2 different masks that can be interleaved to get the original pattern as desired. and the masks are identified by assigning colors to the metals (red and green as shown in the following figure). Since the masks are fabricated separately this can be corrected. This way we can get better resolution and higher layout density.