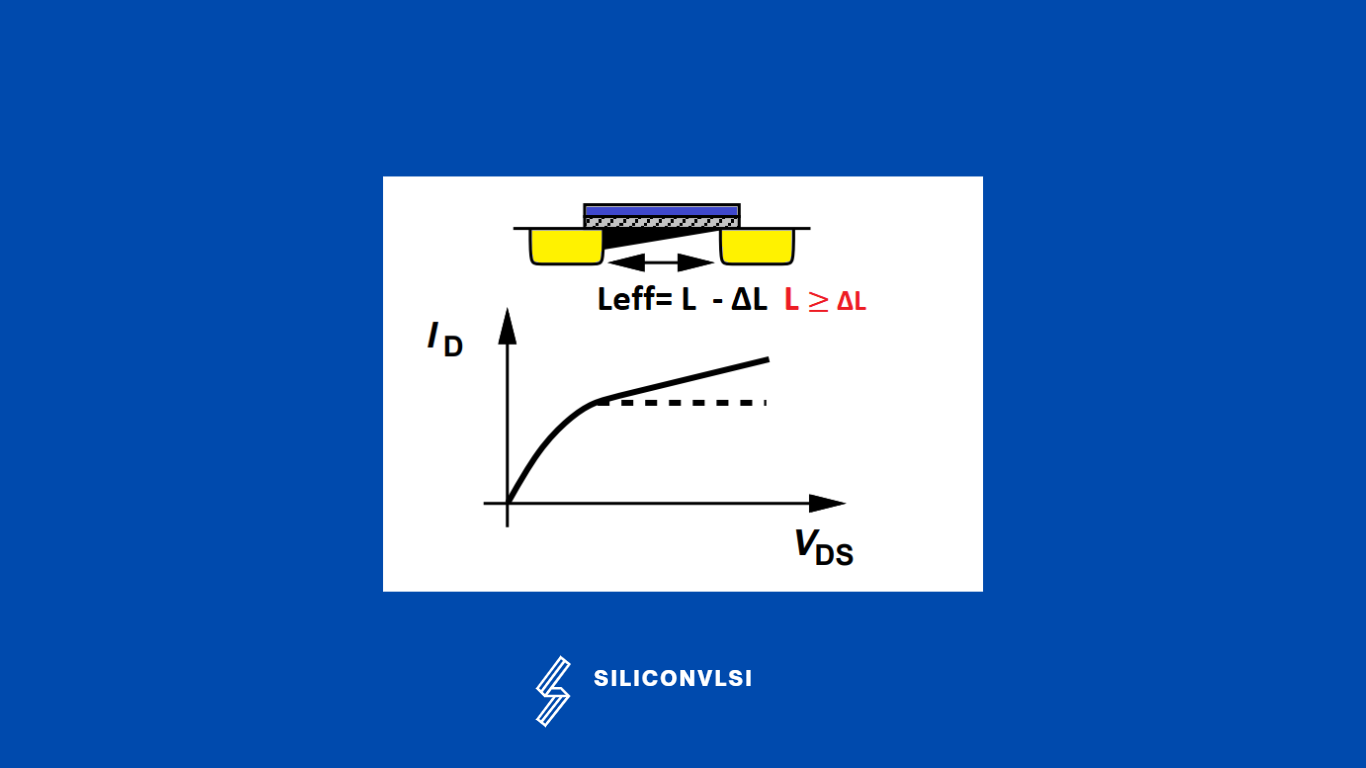
Channel Length Modulation
Channel-length modulation arises from the shortening of the effective channel length of the transistor because of the increase in the drain depletion region as the drain voltage is increased. The resulting channel length is simply equal to the metallurgical channel length minus the source and drain
channel length modulation expression
Because of channel-length modulation, the saturation-region drain current will rise somewhat in response to an increase in the drain-to-source voltage. For FETs with channel lengths larger than, say, 2 µm, this modified drain-current formula is a first-order approximation that is reasonably correct.
![]() depletion region widths. The channel length is another parameter that influences the threshold voltage. For very short channels, the depletion regions of the drain and source junctions are dominant. So overall channel length becomes small Turning the transistor on becomes easier, thus causing a reduction in the threshold voltage.
depletion region widths. The channel length is another parameter that influences the threshold voltage. For very short channels, the depletion regions of the drain and source junctions are dominant. So overall channel length becomes small Turning the transistor on becomes easier, thus causing a reduction in the threshold voltage.
In a triode, the gate-to-source voltage is high enough to permit current flow from the drain to the source, and because of the way the induced channel is constructed. Gate-to-source voltage and drain-to-source voltage have an impact on the drain current’s size.
The triode zone changes into the saturation region as the drain-to-source voltage rises, at which point the only factors affecting the drain current are the physical properties of the FET and the gate-to-source voltage. The following formula represents the gate-to-source voltage (VGS) and drains current (ID) saturation-region relationship.
The transition to saturation mode occurs because the channel gets “pinched off” at the drain end because of Vds=Vds(sat)
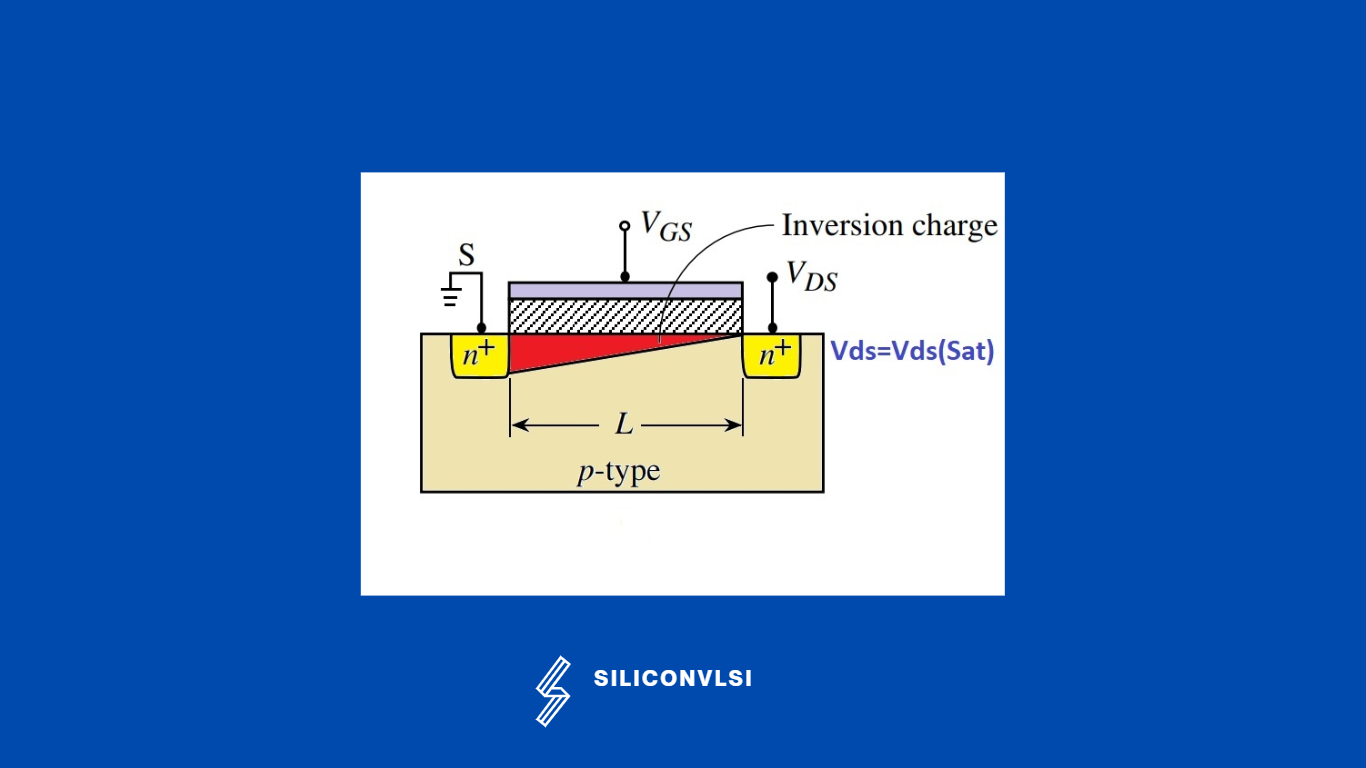
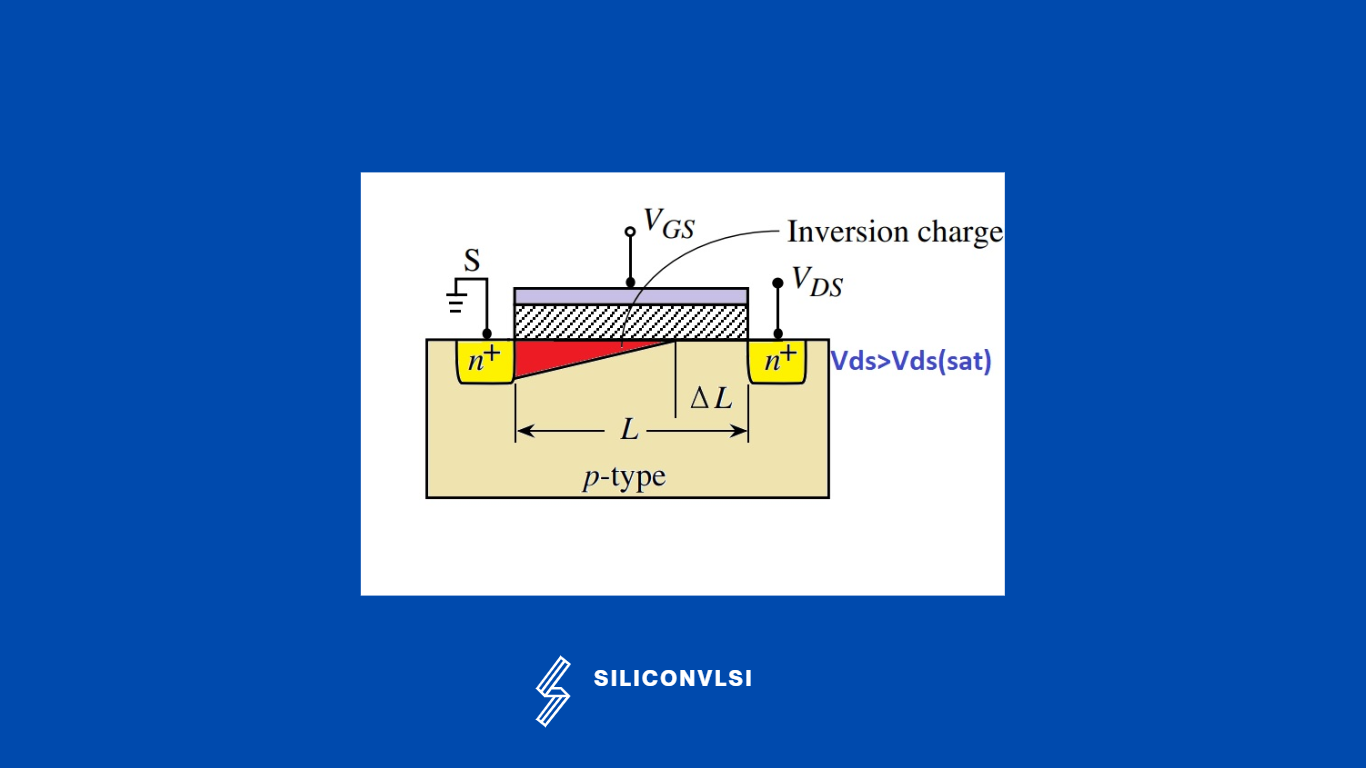
Now if We increase further Vds at the drain not, the channel will start to move further towards the source region, and the Id will be constant because of the High electric field and depletion region.
Channel length Modulation Current Equation
The actual channel length will become Leff= L -DeltaL
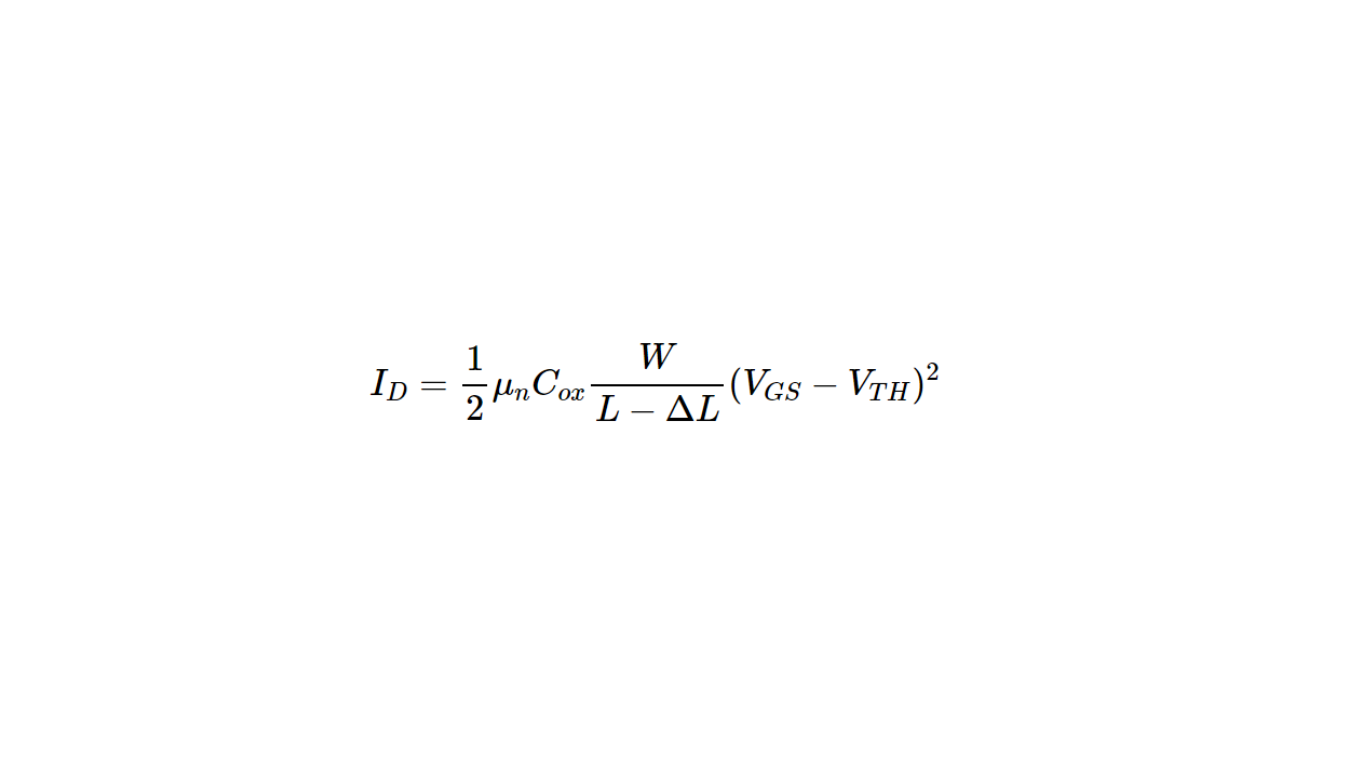
The ratio of the channel’s width toward its length determines the resistance; decreasing the length results in lower resistance and, consequently, higher current flow. The saturation-region drain current will therefore increase slightly as the drain-to-source voltage rises due to channel-length modulation.
As a result, we must adjust the saturation-region drain-current expression to take channel-length modulation into account. To do this, we modify the first statement to include the progressive channel-length reduction
Long Channel and Short Channel device
In the Long channel device, channel length modulation is not more significant, because in Leff= L – ΔL, ΔL is very small, as compared to L.
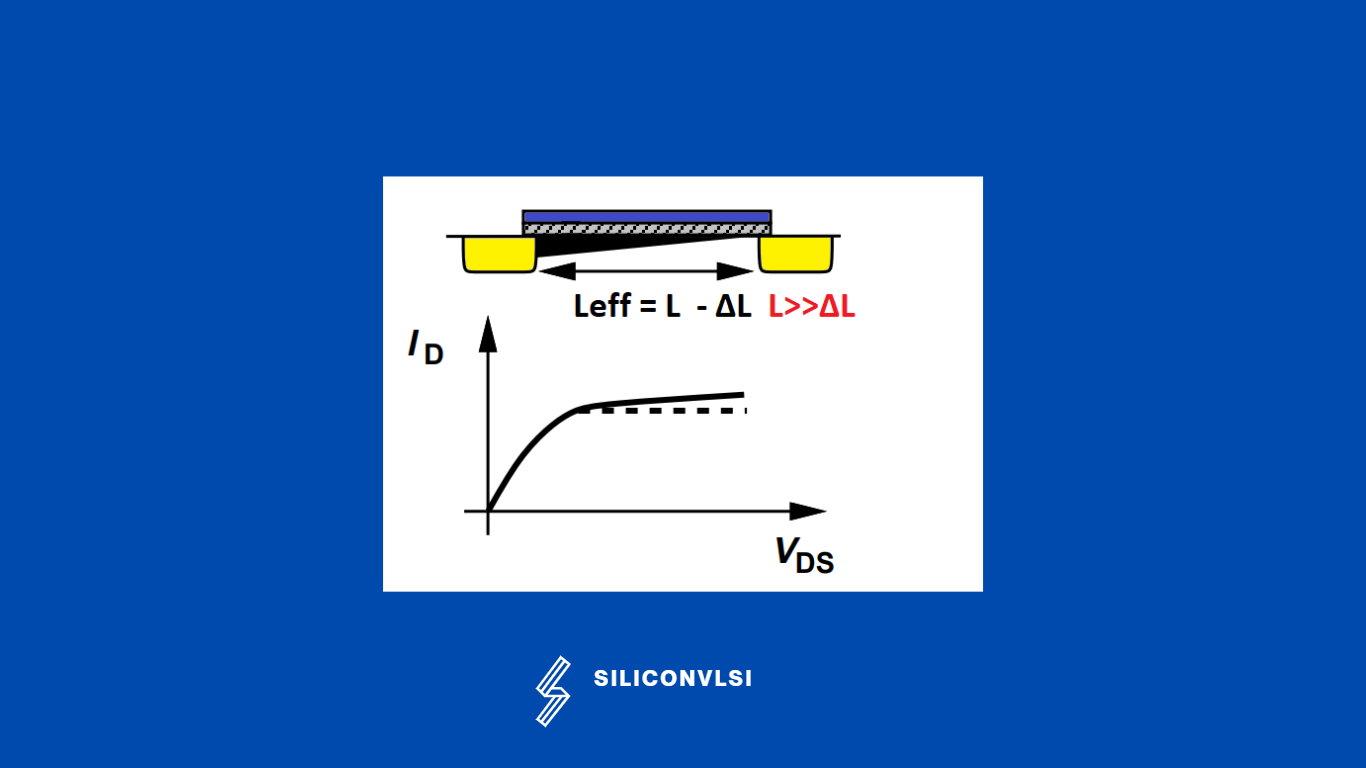
In the Short Channel device, channel length modulation is more significant, because in Leff= L – ΔL, ΔL is and L has not much difference.
Generally, Short Channel devices are not used in Analog Layouts because of channel length modulation.
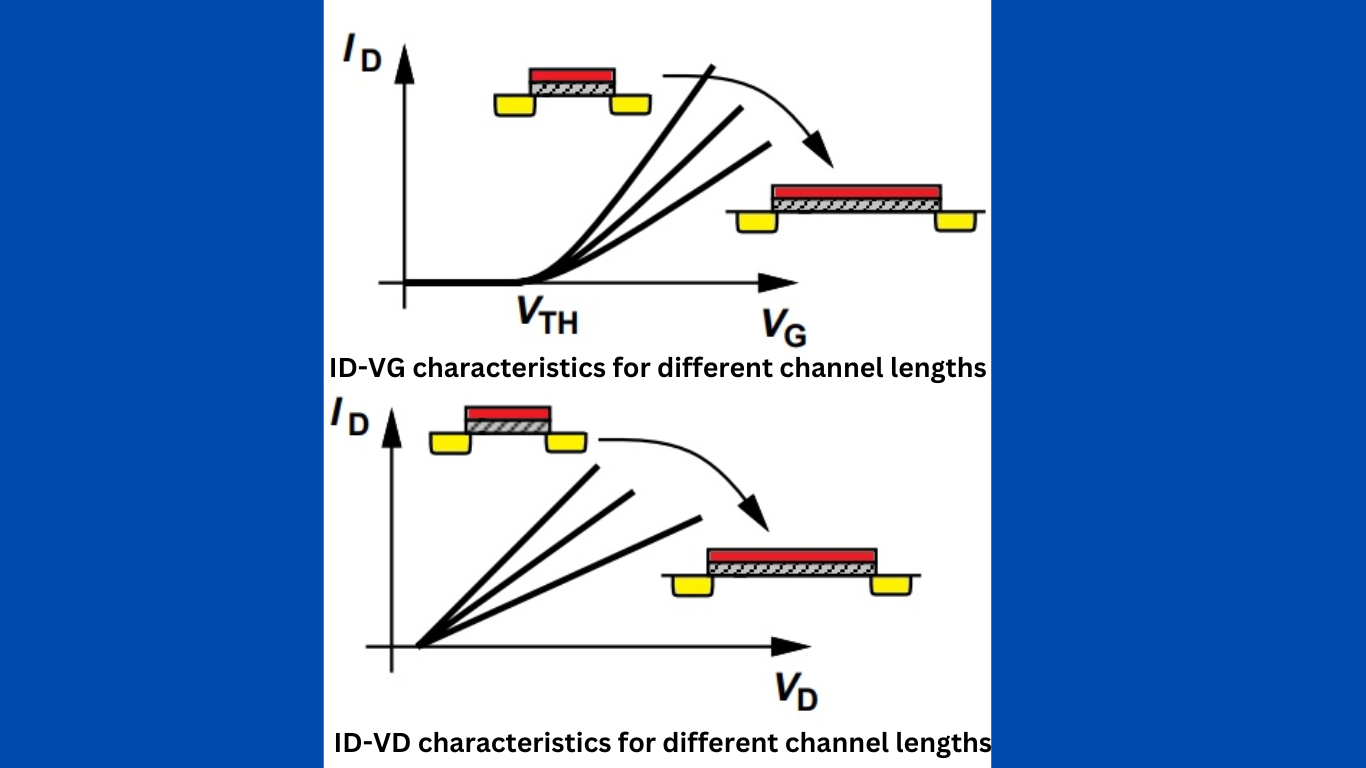
Characteristics for different channel lengths
As the channel length increases, for VG > VT H, the drain current begins with lesser values as the channel length increases, Similarly, ID exhibits a smaller slope as a function of VD. It is therefore desirable to minimize the channel length so as to achieve large drain currents—an important trend in MOS technology development.
What is punch-through?
When the channel length is very small, punch-through occurs. Below this scenario, the source and drain depletion areas might touch, which would cause the drain current to significantly increase.
The punch-through condition’s origin can be understood in light of the following. The source and drain areas of an n-channel device are both doped n+, while the bulk of the device is p-type. Thus, n+-p junctions are formed between the source and drain regions. For a drain current to flow in the device, the drain must be positively biassed. A noticeable depletion area forms at the junction as a result of the drain n+-p junction being reverse-biased.
[terminal]”Punch through Effect will occur in Short channel devices”[/terminal]